
EDI 867: Product Transfer and Resale Report
What is an EDI 867?
Efficiency and accuracy are paramount in B2B communication. Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) enables trading partners to communicate with each other effectively. EDI 867, also known as the Product Transfer and Resale Report, is among the several EDI transactions that organizations use.
The EDI 867 is an industry-standard electronic document that facilitates the exchange of information related to product transfer and resale between trading partners. It provides detailed data regarding the movement of products and enables efficient tracking, inventory management, and sales reporting. Essentially, it helps streamline supply chain operations and ensures accurate record-keeping throughout the product lifecycle.
The EDI 867 transaction is primarily used in settings and scenarios where products are transferred, returned, or resold between different entities within the supply chain. These include:
- Retail industry
- Intercompany transfers
- Wholesale distribution
- Vendor-to-retailer transfers
- Consignment sales
- Third-party logistics (3PL) operations
What is the difference between EDI 867 and EDI 852?
Both EDI 867 and EDI 852 (Product Activity Data) serve the purpose of exchanging product-related information. However, they differ in terms of their specific focus and the scope of data they capture. Here are the key differences between EDI 867 and EDI 852:
Purpose
EDI 867 is specifically designed for reporting product transfers and resale activities between entities within the supply chain. It provides detailed information about the movement of products, including quantities, pricing, and other relevant details.
On the other hand, EDI 852 primarily focuses on reporting product sales and inventory activity. It provides information about sales, stock levels, and related data for specific products.
Scope
EDI 867 tracks the movement of products between different entities, such as intercompany transfers, vendor-to-retailer transfers, consignment sales, and 3PL operations. In contrast, EDI 852 reports sales, inventory, and related activities. It provides data such as item descriptions, quantities sold, pricing, and stock levels at specific locations.
Usage
Trading partners use EDI 867 for internal reporting, inventory management, and supply chain optimization. It enables them to have accurate visibility into the movement of products and supports effective decision-making. At the same time, EDI 852 EDI is widely utilized for sales reporting, demand forecasting, and inventory management. It helps trading partners track product performance and identify trends.
What components does an EDI 867 file have?
An EDI 867 file consists of several essential components, including:
- Header: This section contains general information such as the sender and receiver identification, report date, and version control.
- Summary: It provides a high-level overview of the document, including the total quantities and values of products transferred.
- Detail: This segment contains line-item information, such as product identifiers, quantities, units of measure, and any additional relevant details for each transferred product.
- Summary Trailer: It summarizes the overall information provided in the document, including the total number of detail lines and the total value of the transferred products.
Here is an example of an EDI 867 file:
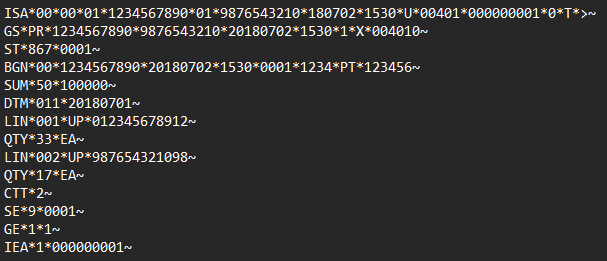
Note: This is for illustration purposes only.
How can I use EDI 867?
If you are involved in the retail industry, EDI 867 can significantly simplify your product transfer and resale processes. However, you need to ensure you have the requisite EDI architecture. Specifically, you will need:
- EDI Capabilities: Ensure that your organization has the necessary electronic data interchange (EDI) capabilities. This includes having EDI software or a dedicated EDI solution in place to generate, send, receive, and process EDI transactions.
- Trading Partner Agreements: Establish trading partner agreements with the entities you will be exchanging EDI 867 transactions with. These agreements define the specific data requirements and business rules for exchanging EDI transactions effectively.
- EDI Communication Methods: Determine the preferred method of EDI communication with your trading partners. This can include various options, such as using a value-added network (VAN), direct point-to-point connections (AS2, FTP, etc.), or web-based portals. Ensure that you have the necessary communication protocols and connectivity established.
- Mapping and Integration: Set up the necessary mappings between your internal systems and the EDI format. This involves aligning the data elements and formats in your internal systems with the corresponding segments and data elements in the EDI 867 transaction. This integration ensures smooth data exchange and enables automated processing of the received EDI transactions.
- Testing and Compliance: Before going all in, test the EDI 867 transactions with your trading partners to ensure data integrity and compliance with their specific requirements. Conduct end-to-end testing to verify that the data is transmitted accurately and is successfully processed by both parties.
EDI 867 transaction example
Let’s take a quick look at an example of an EDI 867 transaction. Suppose that a retailer wants to replenish their inventory by placing a purchase order (PO) with their supplier. To do so, the retailer generates an EDI 850 (Purchase Order) transaction, specifying the products, quantities, pricing, and delivery details.
The supplier receives the EDI 850 from the retailer and generates an EDI 855 (Purchase Order Acknowledgment) in response. This document confirms the acceptance of the PO or provides any necessary changes or adjustments. Additionally, the supplier may choose to generate an EDI 856 Advance Ship Notice (ASN) to notify the retailer about the upcoming shipment.
Upon receiving the products, the retailer performs an internal product transfer to allocate the received inventory to specific locations or stores. To do so, it generates an EDI 867 with the details of the product transfers, including the products, quantities, transfer dates, and relevant identifiers.
What are the benefits of EDI 867?
Implementing EDI 867 can benefit you and your trading partners in multiple ways:
- Improved Efficiency: Automating product transfer and resale processes eliminates manual data entry and saves time for your staff.
- Enhanced Accuracy: By eliminating manual intervention, you reduce the risk of data entry errors and ensure accurate information exchange.
- Streamlined Inventory Management: Real-time visibility into product transfers enables better inventory control, reducing stockouts and improving supply chain planning.
- Faster Order Processing: Automated data exchange speeds up order fulfillment, reducing the time it takes for products to reach customers.
How Astera EDIConnect helps
Modern EDI solutions, such as Astera EDIConnect, empower businesses across industries to optimize their supply chain operations, enhance inventory management, and streamline processes.
EDIConnect is a comprehensive EDI software solution that simplifies the implementation and management of EDI transactions, including EDI 867. Here are some built-in features that make it a valuable tool for your business:
- Translator: EDIConnect’s high-performance streaming EDI translator delivers performance and scalability to process data volumes of all sizes efficiently.
- Validator: Integrated validator performs standard and custom validations seamlessly.
- Transaction Builder: The built-in transaction builder streamlines complex, hierarchical EDI transaction building even for business users.
- Repository Manager: Offers a built-in repository of standard transaction sets.
- Partner Manager: Defines EDI partner information. It includes transaction parsing and information building, such as terminators and date/time formats.
- Automation and Process Orchestration: Defines process orchestration for incoming and outgoing EDI files. Orchestration can be used to download or upload files, generate acknowledgments, invoke data maps, and send emails.
- Intuitive UI: Drag-and-drop, visual mapping interface handles complex hierarchical structures like EDI and extensible markup language (XML) with ease.
Use EDIConnect to simplify the implementation and management of all your EDI documents, ensuring accurate data exchange with your trading partners.



