CDC for ETL Process Optimization in Finance Industry
Every day, customers produce an immense volume of data through hundreds of thousands, if not millions, of individual transactions. From managing customer transactions and financial records to dealing with regulatory requirements and risk management, data plays a crucial role in every aspect of banking operations. This data is categorized as big data, a term denoting “large, diverse sets of information that grow at ever-increasing rates.” To put this into perspective, a staggering 2.5 quintillion bytes of data is generated daily.
Banks rely on Extract, Transform, Load (ETL) processes to make sense of data and extract valuable insights. These processes are critical for banks to manage and utilize their vast amounts of data effectively. However, as data volumes continue to grow and the need for real-time insights increases, banks are pushed to embrace more agile data management strategies. Change data capture (CDC) emerges as a pivotal solution that enables real-time data synchronization and analysis.
Understanding ETL Processes in Banking
ETL refers to the three fundamental steps in data integration. First, data is extracted from various sources, including databases, applications, and external systems. This extraction process involves identifying relevant data points and retrieving them in a structured manner. For example, customer transaction data may be extracted from a database using SQL queries, while regulatory data may be obtained from external systems through APIs.
Next, the extracted data is transformed into a standardized format and cleansed of any inconsistencies or errors. This transformation phase involves applying various data manipulation techniques, such as data validation, cleansing, and enrichment. For instance, if the extracted data contains missing values or outliers, these issues are addressed during the transformation process to ensure data accuracy.
Finally, the transformed data is loaded into a target system or data warehouse for reporting and analysis. The loading phase involves storing the data in a structure that facilitates easy retrieval and analysis. For example, by loading the transformed data into a data warehouse, banks can perform in-depth analysis, generate reports, and gain valuable insights.
Key Challenges in Current ETL Processes
- Growing volume and velocity of data: With the advent of digital banking, mobile payments, and other technological advancements, banks are generating data at an unprecedented rate. This exponential data growth has created significant demands on traditional ETL processes, which struggle to keep up with the speed and scale required for real-time insights.
- Complexity of data sources and formats: Banks have to deal with structured and unstructured data from various sources, such as transactional databases, log files, social media feeds, and more. Each data source may have its own data format and schema, requiring careful mapping and transformation during the ETL process.
- Need for near real-time data integration: Traditional ETL processes typically operate on a batch basis, meaning data is extracted, transformed, and loaded in predefined intervals (e.g., daily or weekly). However, in an era where timely insights can make a significant difference, banks are looking for ways to reduce the latency in their ETL processes.
Introduction to Change Data Capture (CDC)
To address the challenges faced by banks in optimizing their ETL processes, CDC has emerged as a valuable tool.
What is Change Data Capture?
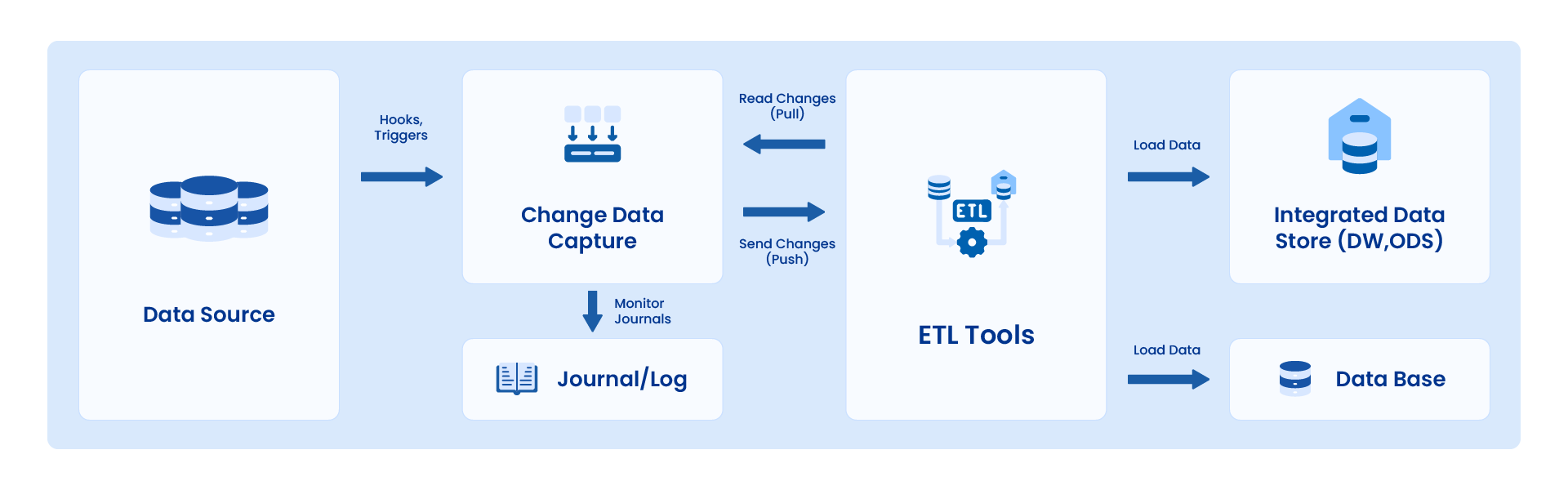
CDC captures the changes (inserts, updates, deletes) made to data at the source system level as events. These events are then propagated to the target system, where they are applied, to keep the data in sync between the two systems.
Imagine a scenario where a customer updates their contact information in the bank’s online portal. Without CDC, the traditional ETL process would extract the entire customer dataset, transform it, and load it into the target system. However, with CDC, only the specific change made by the customer is captured and propagated to the target system. This targeted approach not only saves time and resources but also ensures that the data remains consistent across systems.
Furthermore, CDC provides a granular view of the changes made to the data. Each change is captured as an event, which includes information such as the type of operation (insert, update, delete), the affected rows, and the timestamp of the change. This level of detail allows banks to have a comprehensive audit trail of data modifications.
How CDC Works in Data Integration?
CDC operates by leveraging the transaction logs or change logs present in source systems. By continuously monitoring these logs, CDC technology can identify and capture the changes as they occur. Moreover, CDC allows banks to choose between different synchronization methods, such as one-way replication or bi-directional synchronization, depending on their specific requirements. This flexibility empowers banks to tailor their data integration approach to suit their unique business needs.
Enhancing ETL with CDC
By incorporating CDC into their ETL processes, banks can enhance their data integration capabilities. Traditional ETL processes can be supplemented with CDC technology to capture and replicate real-time data changes. This enables banks to have a more accurate and up-to-date view of their data, leading to more meaningful insights and better decision-making.
When CDC is integrated with ETL, the ETL process can be triggered by the captured data changes, ensuring that the target system is always synchronized with the source systems. This eliminates the need for periodic batch updates and reduces the latency in data integration.
Furthermore, CDC can capture not only changed data but also the metadata associated with said changes. This additional information can be valuable for auditing, compliance, and data lineage purposes.
Steps to Optimize ETL Processes Using CDC
Optimizing ETL processes using CDC requires a systematic approach that considers the unique requirements and challenges of each individual bank. The following steps provide a general framework for banks to implement CDC in their ETL processes:
Identifying Opportunities for Optimization
The first step in optimizing ETL processes is to assess the current state and identify areas for improvement. Banks should conduct a thorough analysis of their existing ETL workflows, data sources, and integration requirements to pinpoint bottlenecks and inefficiencies.
This assessment helps banks identify the specific areas where CDC can bring the most value. For example, banks may find that certain data sources produce a high volume of changes, making them ideal candidates for real-time replication using CDC. By focusing on these high-impact areas, banks can prioritize their optimization efforts and achieve maximum benefits.
During this stage, banks should also consider the scalability and performance requirements of their ETL processes. CDC technology can address these challenges by enabling incremental updates instead of full data loads, reducing the overall processing time and resource consumption.
Implementing CDC in ETL Processes
Once optimization opportunities are identified, banks can proceed with implementing CDC in their ETL processes. This involves deploying CDC technology that is compatible with the bank’s data source and target systems.
When selecting a CDC solution, banks should consider factors such as data source support, scalability, ease of integration, and real-time data replication capabilities. It is essential to choose CDC technology that aligns with the bank’s specific requirements and can seamlessly integrate into the existing ETL infrastructure.
Additionally, banks need to establish data mapping and transformation rules to ensure that the captured changes are correctly applied to the target system. This step involves defining the mapping between the source and target data structures, handling data type conversions, and resolving any conflicts or inconsistencies.
Properly configuring and setting up CDC technology is crucial for seamless data integration and synchronization. Banks should also test the CDC implementation to ensure that it meets the desired performance, reliability, and data quality requirements.
Furthermore, banks should consider implementing data validation and reconciliation mechanisms to ensure the integrity and consistency of the replicated data. This involves comparing the source and target data sets to identify and resolve any discrepancies.
Automated Tools for ETL and CDC in Banking Operations
Adopting automated tools for ETL and CDC processes is instrumental in managing and processing vast volumes of data with precision and agility. These tools offer a sophisticated framework for extracting data from heterogeneous sources, transforming it to meet specific banking requirements, and seamlessly loading it into the target systems. Moreover, CDC capabilities ensure real-time modification tracking within critical datasets, enabling banks to promptly identify changes in transactional records, customer profiles, or compliance standards. By leveraging automated tools for ETL and CDC, banks optimize operational efficiency, streamline data workflows, and maintain a competitive edge in an increasingly data-driven financial landscape.
Centerprise can make building CDC-enabled ETL pipelines easy and fast!
Powered by a no-code interface, Centerprise makes creating and automating ETL pipelines super simple, with increased time and cost-savings. Give it a try!
Book FREE trialUsing Astera to Easily Set Up An ETL Pipeline With CDC
Astera’s user centric approach, code free environment, and intuitive UI allows it to empower business users in their data-driven endeavors.
Here’s a breakdown Astera’s key features for CDC-enabled ETL:
- Diverse Connectivity: Supports a broad range of connectors for popular databases, data warehouses, and file formats, facilitating seamless integration into the ETL process.
- Unified CDC Management: Consolidates CDC oversight for relational databases within a single platform, eliminating the need for separate management, and ensuring comprehensive control across all relevant databases.
- Built-in Transformations: Offers built-in transformation capabilities, empowering users to cleanse and manipulate data effortlessly, enhancing data quality and accuracy within CDC-enabled pipelines.
- Data Profiling and Quality Assurance: Provides robust data profiling and quality features, facilitating checks to ensure accuracy and reliability, which is especially crucial for real-time or near-real-time data processing scenarios.
- Automation and Job Scheduling: Accelerates data transfer through automation and scheduling features, optimizing the efficiency of CDC-enabled ETL pipelines. This includes scheduling near real-time job runs. By incorporating scheduling options like ‘Continuous,’ Astera ensures timely updates and synchronization across data sources.
- Comprehensive Security Protocols: Astera prioritizes data security through robust measures such as bearer token authentication, granular user access control, customizable role-based management, and seamless integration with Windows Active Directory.
In conclusion, leveraging CDC is a pivotal strategy for banks to streamline and optimize their ETL processes. By capturing and processing only altered data, CDC minimizes redundancy, enhances efficiency, and ensures real-time synchronization across systems.
Transform your bank’s data management with Astera’s powerful CDC-enabled ETL workflows. Secure, streamline, and synchronize data effortlessly. Sign up for a demo or a 14-day- free trial now!


