Data Ingestion vs. Data Integration: Understanding the Key Differences
Understanding the difference between data ingestion and data integration is a prerequisite to building efficient data pipelines. While both these processes deal with moving and utilizing data, they represent distinct stages and serve different purposes within your data strategy. Designing each stage appropriately based on its specific function—ingestion for fast intake, integration for structured usability—leads to data pipelines that deliver valuable, analysis-ready data.
You might already be familiar with the broad scope of data integration from our previous deep dive. Now, let’s zoom in on how data ingestion fits into the picture and specifically contrast these two essential processes.
Data Ingestion vs. Data Integration: The Core Differences Summarized
Here’s the TL;DR of data integration vs. data ingestion:
-
Data ingestion involves connecting to source systems, extracting raw data, and loading it into a staging area or data lake.
-
Data integration involves cleaning, transforming, matching, mapping and consolidating that ingested data across sources to create a consistent, analysis‑ready dataset.
Organization generate and collect vast amounts of data, but is it actually fueling better decisions? The journey from raw, disconnected data points to clear, actionable insights depends heavily on a well-architected data pipeline. In other words, getting data into your systems (ingestion) is only the starting point. Making sense of that data by cleaning, structuring, and combining it (integration) is where you unlock actual value.
Here’s a summarized comparison table illustrating the differences between data ingestion and data integration:
| Data Ingestion | Data Integration | |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Aim | Moving raw data from source to landing zone. | Combining & transforming data for a unified view. |
| Data State | Raw or minimally changed. | Transformed, cleansed, structured, enriched. |
| Scope | Often the initial step in a data pipeline. | A broader process, often including ingestion. |
| Timing | Requires intermediate storage for staging and transforming data, called staging area. | Involves or follows transformation. |
| Complexity | Primarily logistical (movement, connection. | Involves business logic, rules, data modeling. |
| Typical Destination | Data lake, staging area, raw storage. | Data warehouse, data mart, analytics platform. |
E-Book: The Must-Haves of Modern Data Pipelines
Building a modern data pipeline architecture for your organization? Make sure it has the requisite key features. Download this free e-Book to learn more.
Download e-BookWhat is Data Ingestion? The First Step in the Data Journey
Data ingestion is fundamentally about moving raw data from its various origin points (like databases, applications, IoT devices, logs, social media feeds) into a target storage system. Think of it as collecting all the raw materials before you start refining them.
- Goal: To transport data efficiently from source to a landing zone, often a data lake, staging database, or cloud storage bucket.
- Data State: The data typically remains in its original, raw, or near-raw format. Minimal transformation, if any, occurs during ingestion.
- Focus: Speed, reliability, and handling diverse data types and velocities (batch, real-time streaming).
- Analogy: Receiving letters and packages from many senders at a central mail sorting facility. The immediate job is just to get them into the facility reliably.
Common data ingestion methods include batch processing (moving data in scheduled chunks) and real-time or streaming ingestion (moving data continuously as it’s generated).
Related: Learn about the differences between batch and stream processing.
What is Data Integration? Creating a Unified View (A Quick Recap)
As covered in our detailed guide, data integration is a broader process focused on combining data from disparate sources to create a unified, consistent, and valuable dataset. It’s about making sense of the collected data and preparing it for analysis.
- Goal: To provide a consolidated view of data for analytics, reporting, business intelligence (BI), and other applications.
- Data State: Involves significant transformation, cleansing, structuring, and enrichment of data. Raw data becomes refined information.
- Focus: Data quality, consistency, accuracy, and creating a cohesive structure (e.g., a schema in a data warehouse).
- Analogy: Taking the collected mail, opening it, sorting it by recipient or topic, standardizing addresses, correcting errors, and delivering it in an organized way so the recipient can easily understand and use the information.
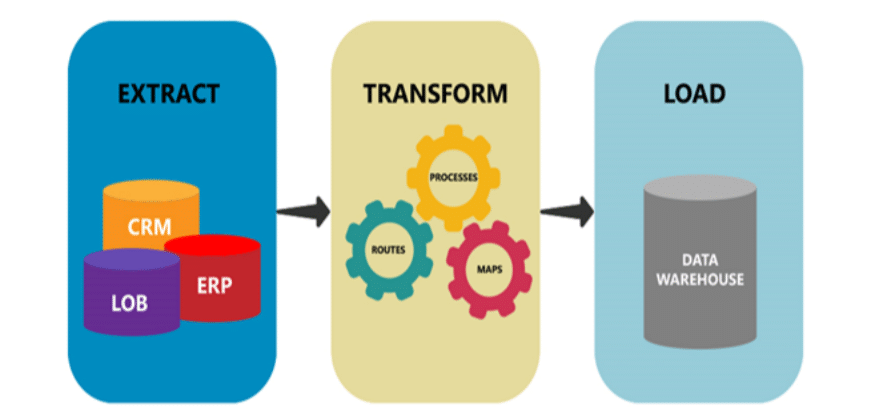
Data integration often involves techniques like ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) or ELT (Extract, Load, Transform).
How Do Data Ingestion and Integration Work Together?
They aren’t mutually exclusive; they are often sequential parts of a larger workflow, orchestrated via data integration tools.
- Ingestion First: Data is ingested from various sources into a central repository. The goal here is to centralize disparate data, making it accessible for further processing.
- Integration Follows: Data integration processes then access this ingested data. They clean it, transform it according to business rules, combine datasets, and load the refined information into a system optimized for analysis, like a data warehouse.
In an ELT paradigm, ingestion handles the ‘E’ (Extract) and ‘L’ (Load) into the landing zone (often a data lake), and integration handles the ‘T’ (Transform) within or downstream from that landing zone. In traditional ETL, ingestion might be seen as the ‘E’, with transformation (‘T’) happening before the final ‘L’ (Load) into the destination (often a data warehouse), making the integration process encompass both ‘T’ and ‘L’.
When Should Your Focus Be on Ingestion?
Prioritize optimizing data ingestion when:
- You need to quickly gather large volumes of raw data from diverse sources.
- You are building a data lake to store raw data for future, potentially undefined uses.
- Dealing with high-velocity streaming data is essential.
- You employ an ELT strategy where transformation happens after loading raw data.
When Should Your Focus Be on Integration?
Prioritize optimizing data integration when:
- The primary goal is reliable reporting and business intelligence.
- Data consistency, accuracy, and quality across sources are paramount.
- You need to combine structured and unstructured data for a complete view.
- You are building or populating a data warehouse or data mart.
- Complex business rules need to be applied to standardize data.
Data Ingestion vs. Data Integration Recap
While data ingestion focuses on the crucial first step of moving raw data, data integration tackles the complex task of transforming and unifying that data into actionable insights. Ingestion gets the data through the door; integration makes it useful. Recognizing the distinct role of each allows you to architect more robust, scalable, and effective data pipelines to power your business decisions.
E-Book: The Must-Haves of Modern Data Pipelines
Building a modern data pipeline architecture for your organization? Make sure it has the requisite key features. Download this free e-Book to learn more.
Download e-BookStreamline Data Ingestion and Integration with Astera
Astera believes data integration and management should be approachable for everyone, no matter their technical acumen. This is why we offer Astera Data Pipeline Builder, an AI-powered data platform, to automate the entire data pipeline building process from end to end. Here’s how Astera Data Pipeline Builder helps organizations:
- Ingest and integrate data from 100+ sources, including databases, cloud platforms, APIs, and more
- Manage ETL, ELT, APIs, and data preparation workflows within a single, unified platform
- Execute tasks and build pipelines with simple English language commands
- Automatically map and align data fields across sources and destinations
- Handle batch and near real-time processing, as well as real-time streaming
- Empower everyone to create and manage their own data pipelines
- Use built-in monitoring tools to track performance and improve
And much more—all without writing a single line of code.
Ready to ingest and integrate enterprise data? Sign up for a free demo or contact us today!
 Astera AI Agent Builder - First Look Coming Soon!
Astera AI Agent Builder - First Look Coming Soon!