
EDI 148 Report of Injury, Illness, or Incident
EDI 148 transaction set, also called Report of Injury, Illness, or Incident, is part of the Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) system. It standardizes information exchange to facilitate the reporting of accidents and injuries. Doing so minimizes the risk of errors and inaccuracies and allows providers and insurers to benefit from a more efficient, automated process.
Here’s a closer look at EDI 148, its components, and format.
What is EDI 148 Report of Injury, Illness, or Incident Transaction Set?
An EDI 148 transaction set provides information regarding an injury, illness, or incident to individuals interested in this information for statistical purposes or legal claims.
The data contents and format of the EDI 148 Report of Injury, Illness, or Incident transaction set are used for the electronic interchange of information. It is divided into segments and data elements, which include the following:
- Nature of injury, illness, or incident
- Cause of injury, illness, or incident
- Date of injury, illness, or incident
- Time of injury, illness, or incident
- Binding terms and conditions
Workflow for the Exchange of an EDI 148 File: Report of Injury, Illness, or Incident Transaction Set
The transaction set EDI 148 falls under X12N Insurance. It is interchanged between parties interested in the information to fulfill statistical, legal, and risk management processing requirements.
EDI X12 148 File Format Sample
The basic EDI X12 148 file format is as follows:
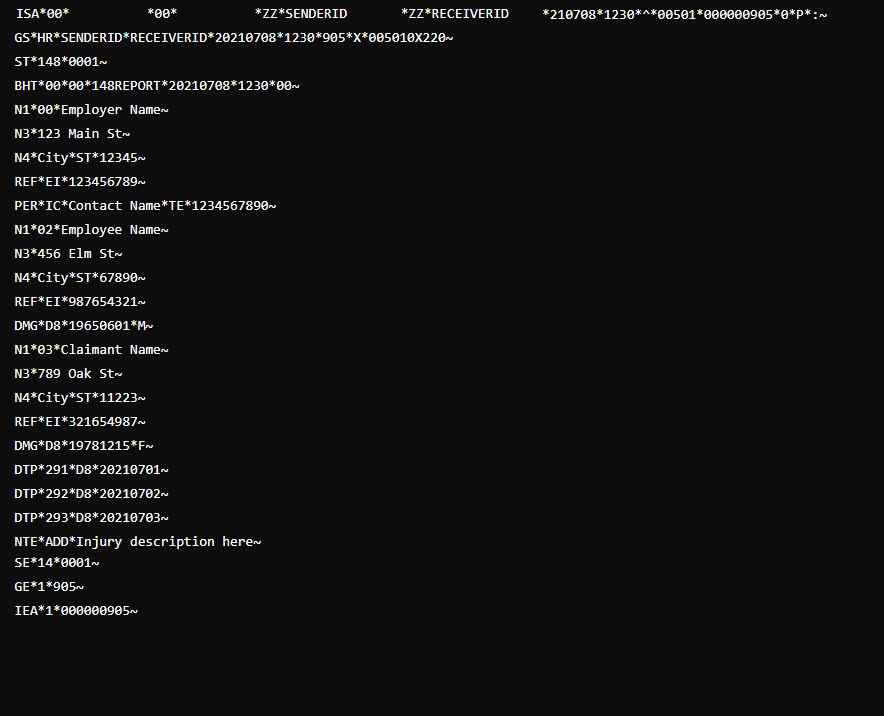
This version includes the core components required to report an injury, illness, or incident.
EDI 148 Specification and File Components
The EDI X12 148 transaction set includes various segments and elements for reporting detailed information about injuries, illnesses, or incidents to stakeholders such as insurance companies or regulatory agencies.
Commonly used versions include 005010X220, but other versions may also be implemented depending on the specific requirements.
File Components
1. Interchange Control Segments:
ISA (Interchange Control Header) identifies the start of an interchange of one or more functional groups and provides sender and receiver identification.
IEA (Interchange Control Trailer) Indicates the end of an interchange and provides control totals.
2. Functional Group Segments:
GS (Functional Group Header) indicates the beginning of a functional group of related transaction sets.
GE (Functional Group Trailer) indicates the end of a functional group and provides control totals.
3. Transaction Set Segments:
ST (Transaction Set Header) identifies the start of the transaction set.
SE (Transaction Set Trailer) indicates the end of the transaction set and provides control totals.
4. Body Segments:
BHT (Beginning of Hierarchical Transaction): Provides hierarchical transaction information such as the report date and time.
Involved Party Information:
- N1 (Name): Identifies a party by type of organization, name, and code.
- N3 (Address Information): Specifies the address of the entity.
- N4 (Geographic Location): Provides geographic location details.
- REF (Reference Identification): Contains reference identification numbers.
- PER (Administrative Communications Contact): Identifies a person or office for communication purposes.
Demographic and Incident Details
- DMG (Demographic Information): Provides demographic details of individuals involved.
- DTP (Date or Time or Period): Specifies dates related to the incident, such as the report date, incident date, etc.
- NTE (Note/Special Instruction): Provides additional information or special instructions.
Claim and Insurance Information
- SBR (Subscriber Information): Provides information about the insurance subscriber.
- NM1 (Individual or Organizational Name): Identifies individuals or organizations related to the claim.
- CLM (Claim Information): Contains details about the claim, including amounts and claim status.
- HI (Health Care Information Codes): Provides health care service codes related to the claim.
- SV1 (Professional Service): Details professional services rendered.
- SV2 (Institutional Service): Details institutional services rendered.
- PWK (Paperwork): References supporting documentation for the claim.
Key Components and Their Roles
| ISA and IEA Segments | Ensure proper routing and identification of the interchange. |
| GS and GE Segments | Group-related transaction sets for logical processing. |
| ST and SE Segments | Mark the boundaries of the transaction set and provide control totals. |
| BHT Segment | Establishes the context and timing for the transaction set. |
| N1 to N4 Segments | Identify and locate involved parties (e.g., employer, employee, claimant). |
| REF and PER Segments | Provide additional identifiers and contact information. |
| DMG Segment | Collects demographic data for individuals. |
| DTP Segment | Specifies critical dates (e.g., injury date, report date. |
| NTE Segment | Allows for descriptive notes about the incident. |
| SBR and NM1 Segments | Capture insurance and personal identification information. |
| CLM Segment | Contains comprehensive claim details, such as service dates and monetary amounts. |
| HI and SV1/SV2 Segments | Detail the healthcare services provided and their codes. |
| PWK Segment | References any additional paperwork or documents relevant to the claim. |
Ensuring Secure and Standardized Data Exchange with EDI Compliance
Adhering to the EDI 148 specifications allows organizations to ensure accurate and efficient reporting of workplace incidents, streamline communication between parties, and facilitate regulatory compliance.
Astera EDIConnect’s message parser, validator, and transaction builder enable it to handle transaction sets in X12 and EDIFACT formats. This allows businesses to stay EDI compliant and easily exchange documents with trading partners or other stakeholders for legal, statistical, claims, and risk management purposes.
Using EDIConnect, users can automate file uploads and downloads, create workflows, and transform files into the required format without investing heavily in developer resources. It creates a more streamlined, error-free workflow that ensures accurate and consistent reporting.
Discover how EDIConnect can transform the way your business handles EDI 148 transactions. Schedule a demo or get in touch for more information.
EDIConnect: A Tried and Tested, All-in-One EDI Solution
Find out more about the industries we’ve helped and how we did it.
Contact Us
