
HR Analytics – The Key to Efficient Talent Hiring and Retention
Data-driven talent acquisition is the new rave among HR professionals. The modern enterprise relies on data for most of its decision-making – from marketing to financial analytics, all managers make decisions based on facts and reliable data. With this increasing reliance on data, even seemingly instinctive decisions such as hiring a new resource or structuring the onboarding process require robust data pipelines.
According to a report published by the Society of Human Resource Management (SHRM), the cost of a poor hire can amount to $240,000. An investigation conducted by Career Builder confirms that 74% of HR professionals have hired the wrong person for a job at least once and that companies lose an average of $14,900 on each poorly filled job vacancy. Such problems led to the need for a foolproof system for making hiring decisions and monitoring employee performance. However, data often exists in silos and unstructured formats, making it difficult to visualize results and develop actionable insights.
Employers no longer need to rely on their ‘gut feeling’ and ‘sixth sense’ to determine whether a particular candidate is suitable for a job vacancy. Today, growth-oriented organizations set on boosting productivity and retention rates use pre-defined metrics and complex data models to govern prospective employees’ hiring and onboarding processes.

An efficient data pipeline can help you make smarter HR decisions.
These types of data-driven objectives are realized through the implementation of a system of Talent Acquisition Analytics or People Analytics. Talent Acquisition (TA) Analytics or People Analytics is the automation of HR processes and the subsequent use of data to assist in the organization’s recruitment process. It involves analyzing different metrics in hiring the most skilled, motivated, and behaviorally apt individuals to fill an organization’s skills and knowledge gaps.
An HR data warehouse is an essential cog in such an architecture. It collects and consolidates data related to recruitment, onboarding and employee performance and updates it in real-time. When fed into an analytics platform this information helps talent acquirers make strategic decisions based on the organization’s needs.
This blog will explain how an HR data warehouse can drive data-based hiring and help you overcome the major challenges involved in HR analytics.
Key Metrics in Talent Acquisition Analytics
Identifying key metrics is usually the first step when performing any analytical process. These metrics are tracked by analytics tools and stored in an HR data warehouse to drive business intelligence. Thus, an HR data warehouse is used to improve the structure of candidate pipelines, spot bottlenecks in the hiring process, and determine the most efficient channels for talent acquisition and onboarding.
Here is an example of how an HR analytics dashboard presents this information in a more easy-to-understand manner:
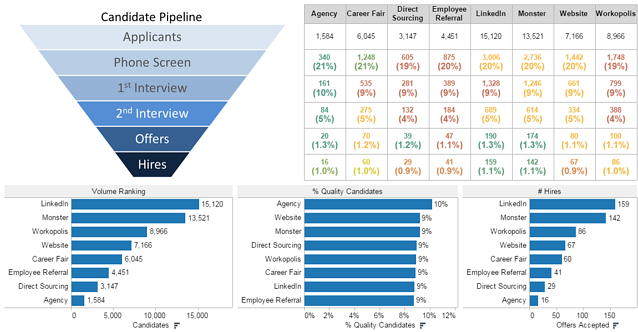
A candidate pipeline BI dashboard is just one of the ways that an HR data warehouse can be used to drive TA analytics. Image taken from peopleinsight.com
Attracting suitable candidates for a job vacancy while minimizing costs on hiring and onboarding is a complicated task that requires great precision in measurement and data collection. While the exact KPIs for talent acquisition might vary in each organization, some standard metrics that are used across a range of industries are:
- Time-to-hire: This is the total time taken from the day the candidate enters the organization’s talent acquisition pipeline to the day they sign their employment contract and take the job. An HR warehouse delivers structured and standardized data to an analytics tool with the aim of identifying bottlenecks so that the time-to-hire can be minimized.
- Cost-to-hire: Cost-to-hire is defined as the total costs incurred during the hiring process divided by the total number of hires. It reflects the organization’s internal and external expenditure on talent acquisition. A consolidated store of data can help recruiters boost efficiency by aggregating cost-to-hire of all new hires, which can then be compared to the subsequent increase in revenue.
- Quality of Hire: The quality of hire is a performance-based metric that tracks the overall success of the hiring process. It is based on the first-year performance ratings of new hires and the extent to which supervisors and line managers are satisfied with a new employee’s work. HR data warehouses can be used to drive a comparative analysis of the overall quality of a new batch of hires and judge whether the right people are being hired.
- Candidate sources: Gives information about how and where the candidate learned about the job and how they applied. The source-of-hire metric can be consolidated in an HR data warehouse to see the effectiveness of different channels for job ads.
- Application completion rate: The application completion rate indicates the number of applicants who were able to go through with the entire application form and compares it to the number of candidates that dropped out after engaging with it to some extent. Recruiters can leverage this data from the HR data warehouse to get insights about what part of the application has the highest dropout rates and fix the application form accordingly.
- Sourcing channel cost: This is the ratio of the advertisement cost per platform for the job ad to the number of successful hires from each source. Sourcing channel cost data can be aggregated in an HR data warehouse and visualized in a BI tool to increase the efficiency of HR expenditure.
Benefits of Using the HR Data Warehouse for Talent Acquisition
According to the 2018 report by Global Recruiters Trend, 50% of recruiters now rank big data as the basis of their hiring strategy. With growing reliance on big data to formulate effective hiring strategies, the benefits of having and maintaining an HR data warehouse are now recognized by managers worldwide. The diagram below summarizes how talent acquisiton analytics can be used to make different business decisions across an enterprise.
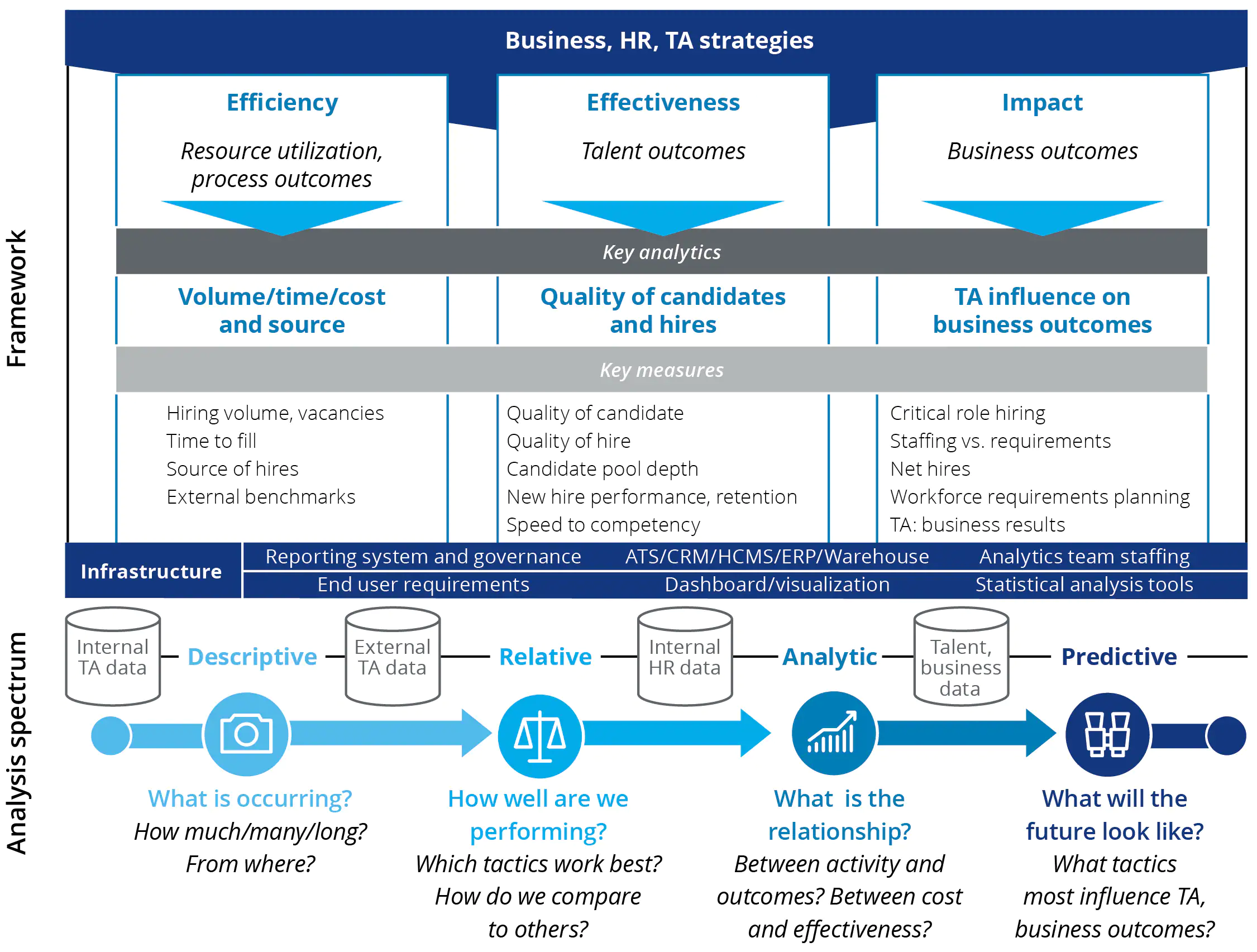
TA analytics from an HR data warehouse can be analyzed to make different business decisions. Image taken from https://www2.deloitte.com/us/en/pages/human-capital/articles/talent-acquisition-analytics.html
Recruiters and HR Managers carry out statistical analyses of the data and visualize significant results on BI dashboards to formulate hiring strategies. For example, application tracking systems are assessed together with feedback tables in an HR dashboard to determine the quality of the hire. In this way, a more data-driven approach in HR operations helps maximize the organization’s efficiency and productivity, identifies bottlenecks in the application process, and allows HR departments to target job ads to highly relevant candidates.
Some of the main benefits of implementing HR analytics include:
- Automating HR and Saving Time: Using ETL processes within an HR data warehouse allows the automation of complex tasks. Users can create dimensional models to track data that is consistently updated while keeping a store of relevant historical data. This saves up the department’s time on accessing old archives of applications and candidate profiles to analyze past data.

Investing in an HR data warehouse significantly optimizes the hiring process.
- Data-based decision making: All the relevant facts, figures and information related to the hiring process are stored in an HR data warehouse. Recruiters can base their analysis of all the relevant KPIs on a single source of truth and decide whether to hire someone based on performance in the application process, their qualifications, and their cost-to-performance ratios. A recent study confirms that 41% of candidates perform better in organizations where recruitment is based on analytics.
- Predictive Analytics: The power of data helps users make near real-time decisions and predict future problems based on current statistics. In an HR data warehouse, data can be leveraged to identify skill and knowledge gaps within the organization by creating data models with employee information and visualizing this data with the help of BI tools. Recruiters can use these insights to make data-driven hiring decisions as the organization grows instead of being forced to make quick, impulsive decisions.
- Improve the Application Process: Job applications are often long, tedious processes that require a lot of work on the part of both the applicant and the recruiter. HR analytics can make applications more focused and the process more streamlined by incorporating feedback from existing employees. For organizations handling public sector onboarding, seamlessly managing government-specific documentation is also essential, and resources covering employment forms for HR teams can provide added efficiency in these processes.
- Ensure Diversity in the Workforce: Demographic data can be extracted from candidate profiles and used to gauge the extent of racial and ethnic diversity in an organization. Data from various sourcing channels often exists in silos, making it difficult for recruiters to check if they are meeting their diversity targets. An HR data warehouse allows recruiters to visualize their current team’s demographic makeup and make future hiring decisions accordingly.
Make Better Hiring Decisions with Astera Data Warehouse Builder
Talent acquisition analytics has vastly expanded the scope of HR functions within an organization. While it has undoubtedly made analytical decision-making more accessible and streamlined, very few organizations have been able to implement it and derive value from it. However, due to its potential to improve business results from increasing retention rates and enhancing employee performance to making the hiring process quicker and more targeted, TA analytics is widely seen as the future of HR.
Astera Data Warehouse Builder can be used to reverse engineer complex HR databases and build data models for visualization in BI tools. With seamless cloud integration capabilities and a robust ETL engine, Astera Data Warehouse Builder provides HR managers a unified platform to manage all their data needs and the ability to access all their TA data in one place.
The corporate world is increasingly based on big data, and HR analytical experts will be skilled and in-demand assets in the future. Recruitment specialists need to equip themselves with the necessary skills to read and understand data based on demographics, geographical information, company size and budgetary constraints to make better and smarter hiring decisions. A metadata-driven data warehouse builder such as ADWB assists them through the entire process. Try out a demo of Astera Data Warehouse Builder today and build your own HR data warehouse in a few simple steps.
 Astera AI Agent Builder - First Look Coming Soon!
Astera AI Agent Builder - First Look Coming Soon!

