Data Fabric: A Complete Guide | Architecture, Benefits & Implementation
What is a Data Fabric?
Data fabric is an architecture that integrates different data systems and tools. It provides unified access to data stored across various locations to organize, manage, and govern it without moving it to a central database or data warehouse or changing its format.
Data fabric relies on metadata to ‘understand’ the data’s structure, lineage, and meaning across various sources. This information enables informed decision-making and optimized data usage. It caters to various applications, including customer insights, regulatory adherence, cloud transitions, data sharing, and analysis.
The Importance of Data Fabric
Data fabric emerged as a response to the growing challenges of managing data in the modern enterprise.
Over the past few decades, organizations have witnessed exponential growth in data volume. This data originates from diverse sources, including traditional databases, customer interactions, social media, and the Internet of Things (IoT) devices. As data sources multiplied, they often became siloed within specific departments or applications.
Data gravity—data becoming difficult and expensive to move as it grows in size—was also a significant barrier to consuming data for analytics. The fragmented data landscape made obtaining a unified view of the organization’s information assets difficult.
These factors create a need for a solution to bridge the gaps between disparate data sources, simplify access, and ensure consistent governance. Data fabric emerged as an architectural framework that addressed these challenges.
It helps businesses use data effectively, regardless of where it’s stored—in the cloud, across multiple clouds, in a hybrid environment, on-premises, or at the edge. It makes data sharing and insight gathering easier by offering a complete 360-degree overview of available data.
The key to data fabric is metadata, which, along with machine learning and artificial intelligence (AI), deep data governance, and knowledge management, enables efficient data handling for better business outcomes.
The Benefits of Leveraging Data Fabric
Data fabric offers businesses many benefits by optimizing self-service data exploration and analytics. It promotes speed and efficiency, which leads to lower costs and more production.
- Solving the issue of data silos by providing accurate and complete insights from different sources, regardless of the location.
- Making data easily accessible speeds up the delivery of business value.
- Ensuring data is trustworthy, secure, and well-managed through automatic governance and knowledge processes.
- Data fabric empowers users to easily find, understand, and utilize data by providing a unified platform that integrates various data processing techniques and tools, such as batch or real-time processing, ETL/ELT, etc.
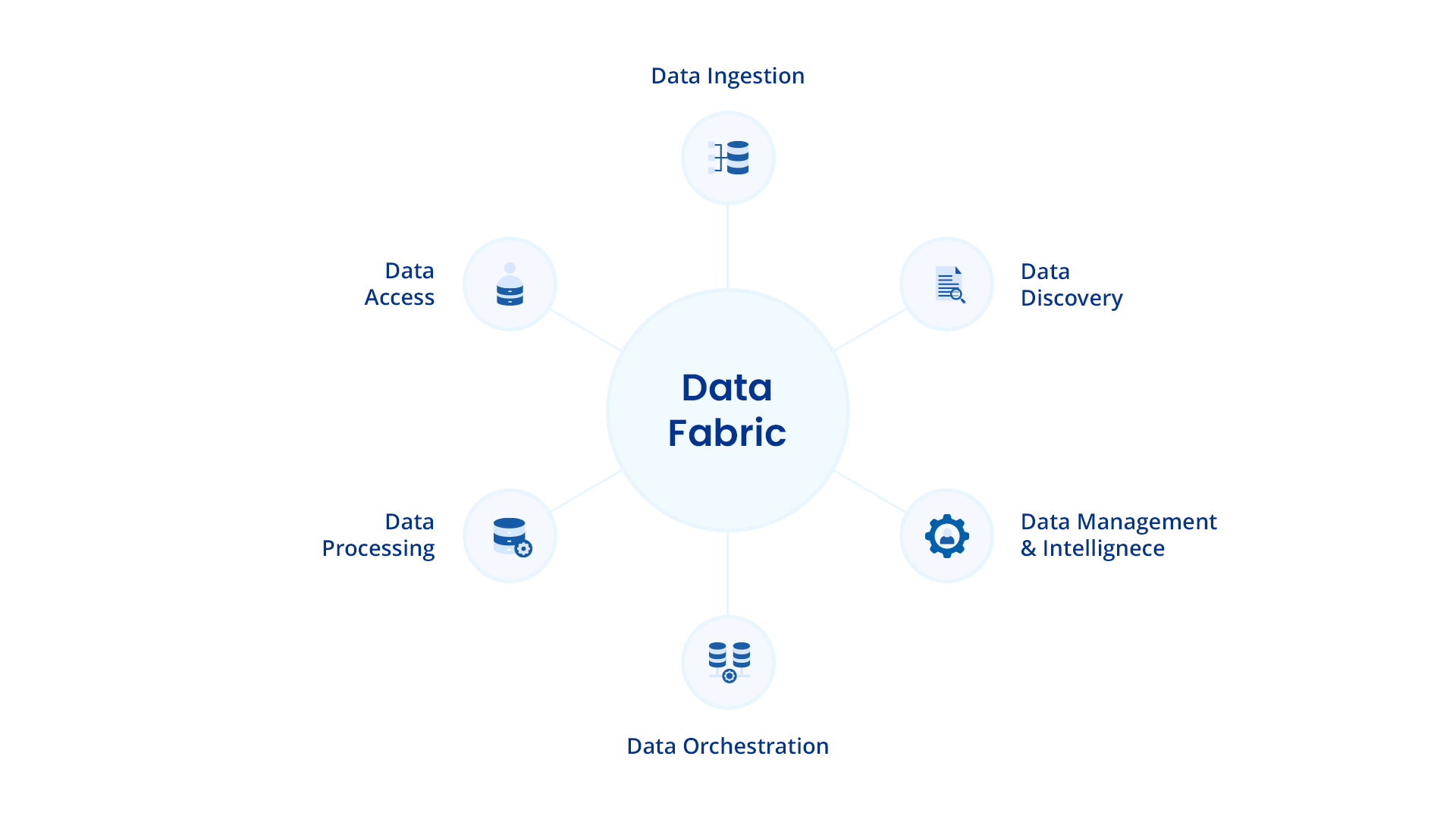
Data Fabric Architecture
The data fabric architecture, with a foundation in metadata and real-time events and an emphasis on easy access to secure and well-managed data, enables automated integration and governance of dispersed data.
Building such an architecture goes beyond just setting up a basic app or using certain technologies. It demands teamwork, alignment with business goals, and strategic planning.
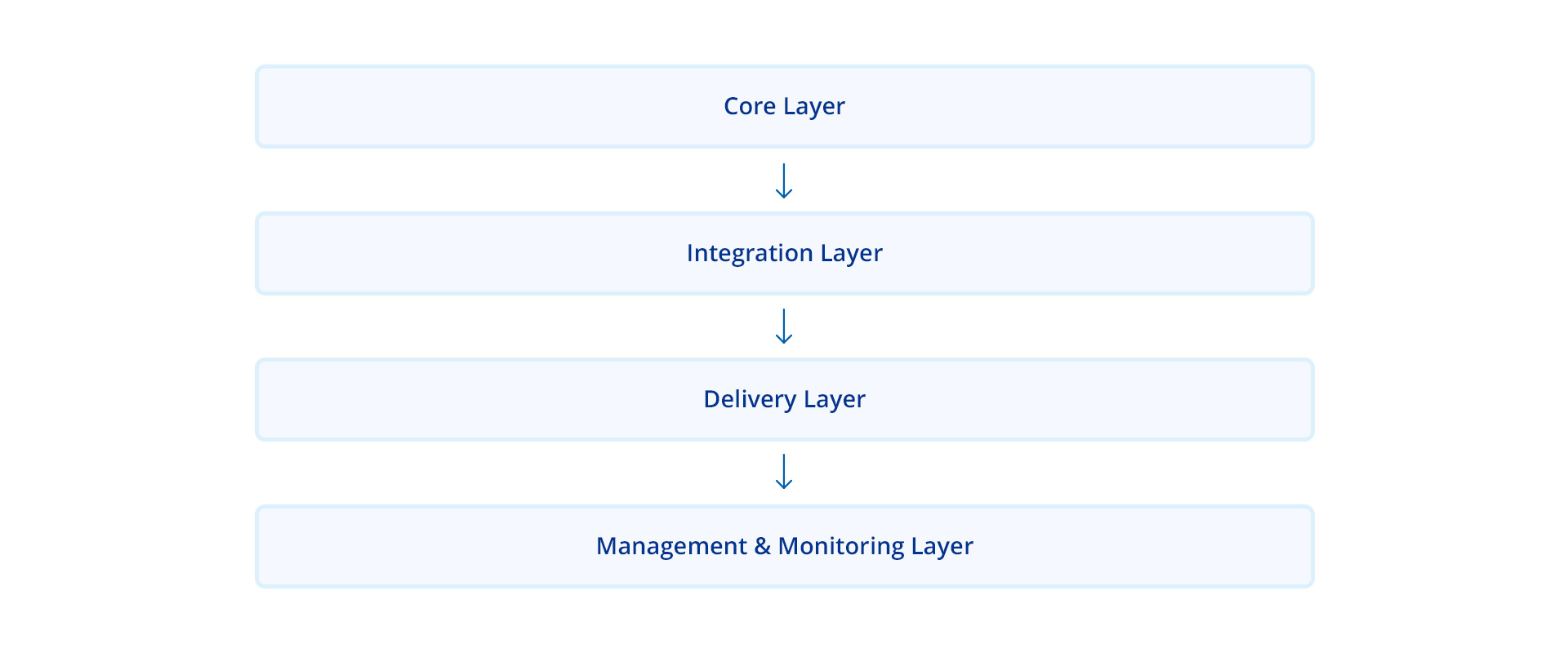
Data fabric effectively manages metadata, allowing for scalability and automation. This makes the architecture capable of meeting expanding business needs and ready to incorporate new tools and technologies in the future. This architecture can be summarized into multiple layers encompassing various components.
1. Core Layer
- This layer establishes a metadata management system, essentially a detailed catalog of all the data assets. The catalog provides information about the data’s origin, format, meaning, and usage guidelines.
- The fabric enforces a set of data governance policies. These policies ensure data quality, consistency, and security across the ecosystem. They define who can access specific data, how it can be used, and establish processes for data lineage (tracking the data’s journey).
2. Integration Layer
- Using the integration layer, data fabric enables users to access and utilize data seamlessly from various sources, both internal and external. This includes data lakes, databases, cloud storage platforms, social media feeds, and even sensor data from the Internet of Things (IoT).
- This layer utilizes data transformation tools to clean, standardize, and enrich the ingested data. It involves removing inconsistencies, converting formats (e.g., changing from CSV to a database format), or extracting specific features from the data.
- It provides a set of APIs (Application Programming Interface), allowing applications and users to access and interact with data from various sources through a consistent interface.
3. Delivery Layer
- The data fabric architecture features a central data catalog that acts as a searchable repository of all available data assets. It provides detailed descriptions and access controls and facilitates easy discovery of the data users need.
- Data fabric enforces secure data access control mechanisms. It determines who can access specific data sets and how they can be used, ensuring data privacy and compliance with regulations.
- Finally, it delivers the prepared data to various applications and users in the required format. This might involve data visualization tools, machine learning algorithms, or business intelligence dashboards.
4. Management and Monitoring Layer
- Data fabric facilitates quality monitoring throughout the lifecycle by integrating with data quality tools. This monitoring includes identifying and rectifying errors, inconsistencies, or missing values.
- The architecture leverages performance monitoring tools within the data ecosystem to track processing speeds, identify bottlenecks, and ensure smooth data flow across the system.
- It prioritizes data security by implementing security measures like encryption, access control, and audit trails.
Data Mesh vs. Data Fabric vs. Data Lake: What’s the Difference?
Data mesh, data fabric, and data lake are three prominent approaches to managing vast amounts of data spread across diverse sources. They all have distinct roles and functions in data management.
| Data Lakes | Data Mesh | Data Fabric | |
| Definition | It acts as a central repository where organizations can dump raw data from various sources, like databases, social media feeds, and sensor readings. | It is a network of self-serving data sources. Each domain within an organization (e.g., marketing, finance) owns and manages its data as a product. | It acts as a layer that simplifies data access and management across diverse sources, regardless of location or format. |
| Function | A central, low-cost storage solution for vast amounts of data. | They are responsible for ensuring data quality, cleaning, and transforming it for use by their specific domain and potentially others. | It provides a unified view of the data, allowing users to find and utilize information from various sources through a single interface. |
| Focus | They offer flexibility for storing any data, even if it’s unstructured or not immediately usable. | Data mesh emphasizes clear data ownership and empowers domain teams to manage their data as a valuable asset. | Data fabric focuses on integration and governance by enforcing policies and ensuring data quality, security, and accessibility. |
| Data Ownership | Ownership of data in a lake can be unclear. | Each domain (department) owns its data and is responsible for its quality, accuracy, and transformation.
|
The data fabric itself doesn’t own the data—it provides the platform for access and governance. Ownership remains with the source. |
| Data Access | Finding specific data in a lake requires technical expertise to navigate and access the data. | Data access is typically limited to the domain that owns it, ensuring focused utilization. | Data fabric offers a unified view and easy access to data from various sources through a central platform. Users can find and utilize data regardless of its original location. |
Data Fabric Use Cases
1. Data Integration
Data fabric helps break down data silos, especially in the finance sector, where it can merge data from various financial systems. It allows data engineers to build compelling data pipelines, improving data access. As a result, finance organizations can get a complete picture of their financial and enterprise data, leading to more informed decision-making.
2. Real-time Data Analytics
Data fabric aids organizations in accessing, integrating, and analyzing data almost in real-time. In healthcare, it allows for the analysis of patient data to improve care, treatments, and outcomes.
3. Data Discovery
Data discovery is an essential part of business analytics, as it helps control access to the right data. It reveals available data, like the “load” step in traditional ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) processes. The power of the data fabric framework comes from its Data Management layer. This layer covers all other layers, covering security, Data Governance, and Master Data Management (MDM), ensuring efficient and secure data handling.
4. Data Governance
With data fabric architecture, organizations can put strong data governance policies in place. This helps them control their data better, ensuring it is accurate, consistent, and secure.
For instance, government bodies can benefit from data fabric and help safeguard sensitive information, like personal details. Improving data accuracy and consistency through data fabric can increase the quality of the data, which leads to more reliable data analyses.
How to Implement Data Fabric
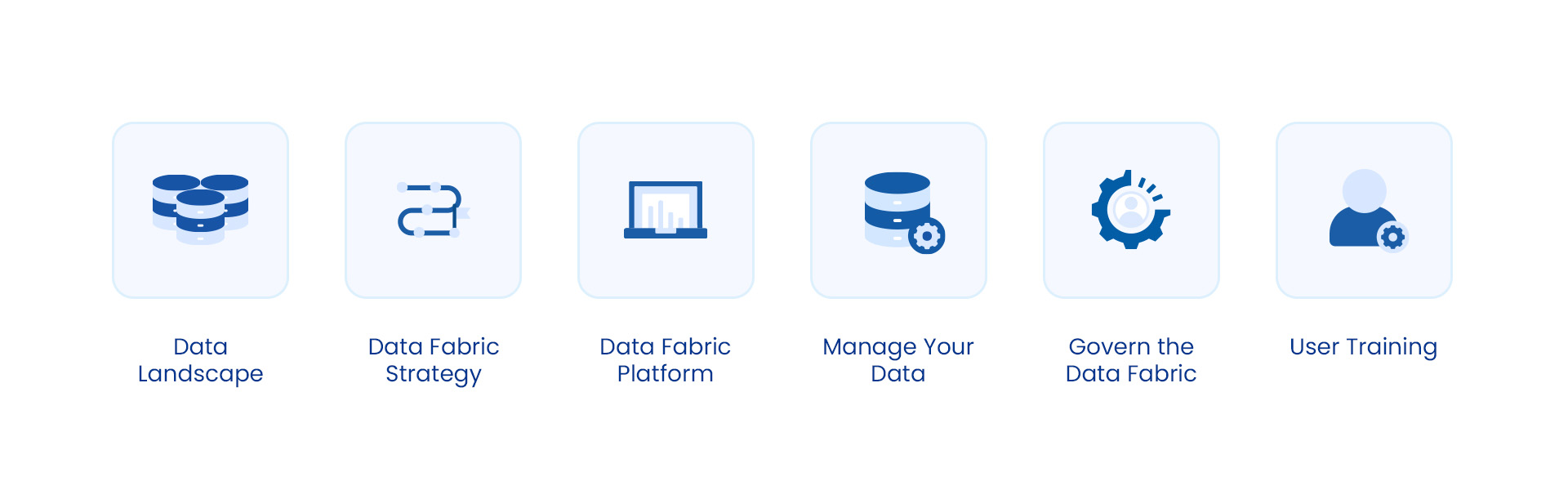
Data Fabric offers a transformative approach to data management, but successful implementation requires careful planning and execution.
1. Data Landscape
- Conduct a comprehensive inventory of all the data sources, both internal and external.
- Evaluate the current state of the data and understand how different user groups within the organization access and utilize data. This understanding helps tailor the data fabric to their specific needs and workflows.
2. Data Fabric Strategy
- Clearly define the objectives to achieve with data fabric implementation. Is it about improving data accessibility, enhancing data security, or streamlining data governance processes?
- To select a data fabric architecture, consider your organization’s size, data volume, budget, and technical expertise.
3. Data Fabric Platform
- Choose the appropriate data fabric tools and technologies that align with the chosen architecture and strategy.
- Integrate data quality and governance practices throughout the implementation process. Data quality ensures the data fabric’s accuracy, consistency, and security from the start.
4. Manage Your Data
- Connect various data sources into a unified platform.
- Implement data transformation tools and establish a centralized data catalog to document and organize data assets.
5. Govern the Data Fabric
- To protect sensitive data, prioritize data security by leveraging data encryption, access controls (role-based access control or RBAC), and audit trails.
- Establish clear data governance policies that dictate your data fabric’s ownership, access control, and usage guidelines.
6. User Training
- Design training programs to educate users on accessing and utilizing data within the data fabric platform.
- Help teams understand of the importance of data quality, responsible data usage, and data security best practices.
Risk Associated with Data Fabric
While data fabric has multiple advantages for data management, it also introduces new security considerations.
Data in Motion
During data movement within the data fabric, sensitive information is vulnerable to interception by unauthorized parties.
To secure the data throughout this lifecycle, organizations can;
- Encrypting data at rest (stored) and in transit (being moved) safeguards its confidentiality even if intercepted.
- Utilize secure communication protocols like HTTPS to establish encrypted connections during data transfer.
Access Control Challenges
If data fabric is not managed effectively, it can create a single point of failure, where a security breach could grant unauthorized access to a vast amount of data.
- Grant users only the minimum level of access needed to perform their tasks.
- Define user roles with specific permissions, restricting access to sensitive data based on job function.
Evolving Cyber Threats
Data fabric systems must adapt and respond to these evolving cyber threats.
- Conduct regular testing and assessments to identify and address potential security weaknesses.
- Implement an SIEM (Security Incident and Event Management) system to monitor security events, detect suspicious activity, and enable a response to potential breaches.
Better Data Management with Astera
Data Fabric is a data management architecture for flexibility, scalability, and automation. It is a unified platform to access, integrate, and govern data from diverse sources. While it offers a powerful approach, its success hinges on efficient data integration and transformation.
Astera provides pre-built connectors, data quality management, data governance, and workflow automation to simplify data preparation and ensure high-quality data flows within your data fabric. It seamlessly connects multiple data sources, regardless of format or location, allowing you to remove data silos and gain a complete view of your data.
Utilizing metadata, Astera delivers automation for all your data management needs, including integration, data preparation, data quality, governance, and master data management. Experience Astera Data Stack with a 14-day free trial or schedule a demo today.
Get Started with Astera Data Stack to Get Unified Data Access
Begin your journey with Astera Data Stack's 14-day free trial. Seamlessly integrate, manage quality, and govern your data for enhanced business insights.
Start a Free Trial Astera AI Agent Builder - First Look Coming Soon!
Astera AI Agent Builder - First Look Coming Soon!