What is Data Modernization? Benefits, Importance & Components
What is Data Modernization?
Data modernization transforms an organization’s data into more usable and accessible formats, making it usable by modern applications and systems, such as cloud-native applications, IoT devices, and mobile applications.
Data modernization also includes extracting, cleaning, and migrating the data into advanced platforms. After modernizing and transferring the data, users access features such as interactive visualization, advanced analytics, machine learning, and mobile access through user-friendly interfaces and dashboards.
Implementing a data modernization strategy enhances data management and governance by unifying data silos, improves the use of intelligence tools, and optimizes data privacy and security through data encryption, access controls, and compliance frameworks across cloud, multi-cloud, and hybrid IT environments.
What is Data-First Modernization?
Data-first modernization is a strategic approach to transforming an organization’s data management and utilization. It involves making data the center and organizing principle of the business by centralizing data management, prioritizing data quality, and integrating data into all business processes. It requires the entire organization, including IT, to prioritize the cultivation, connection, management, analysis, and utilization of data wherever it is located.
A data-first modernization approach directs digital transformation efforts towards creating value centered around data rather than focusing on updating technology infrastructure.
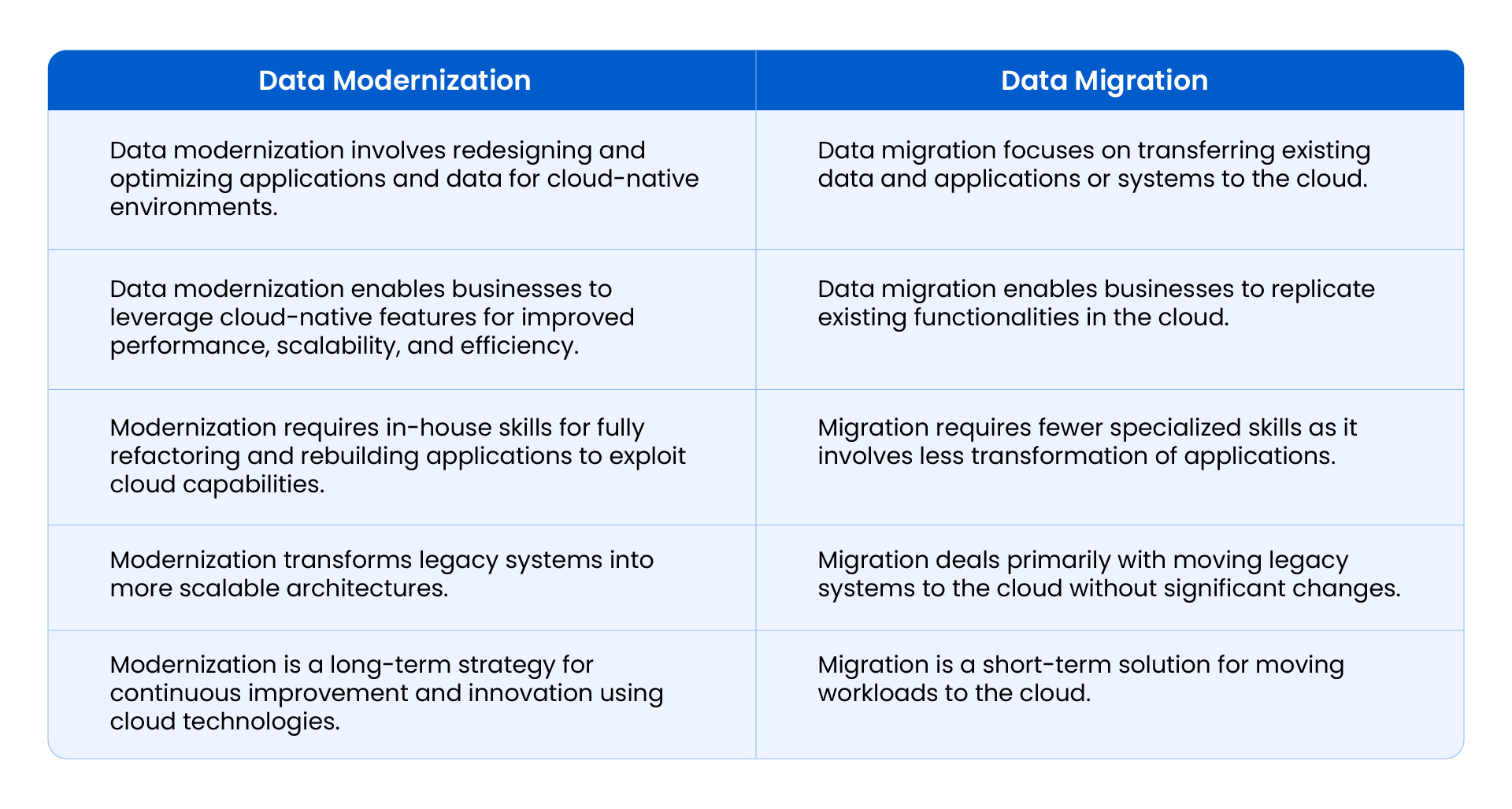
Difference Between Data Modernization & Data Migration
In data modernization, data migration is moving data from the on-premises/legacy systems to the cloud destination. It optimizes these applications or data to use cloud-native architectures and services from cloud providers.
Importance of Data Modernization
Data modernization is about upgrading technology, solving specific business problems, and seizing opportunities that outdated systems cannot address. Modernizing data infrastructure allows organizations to position themselves to secure their data, operate more efficiently, and innovate in a competitive marketplace.
-
Improve Data Access and Usability
Modernizing data infrastructure involves transitioning to systems that enable real-time data access and analysis. The transition includes adopting in-memory databases, data streaming platforms, and cloud-based data warehouses, which facilitate data ingestion, processing, and retrieval. The upgrade allows employees to access and analyze data easily, essential for quickly making informed business decisions.
-
Enhance Customer Experience
Data modernization enables better integration and analysis of customer data by consolidating data from disparate sources into a unified platform. Data integration then facilitates comprehensive customer profiling, segmentation, and personalization, allowing companies to tailor their offerings and communication strategies effectively. This personalization results in higher customer satisfaction and loyalty.
-
Support Advanced Analytics
Modern data systems provide the scalability, performance, and flexibility required to support complex analytics and machine learning workloads. Organizations with a modern data infrastructure can leverage advanced analytics to uncover insights, predict trends, and make data-driven decisions.
-
Reduce IT Costs
Maintaining and operating outdated systems is expensive due to high maintenance costs and frequent repairs. On the other hand, modern data systems are more cost-effective as they reduce the need for ongoing support and offer better performance. The cost-effectiveness of these data systems leads to a lower total cost of ownership and frees up resources for other business investments.
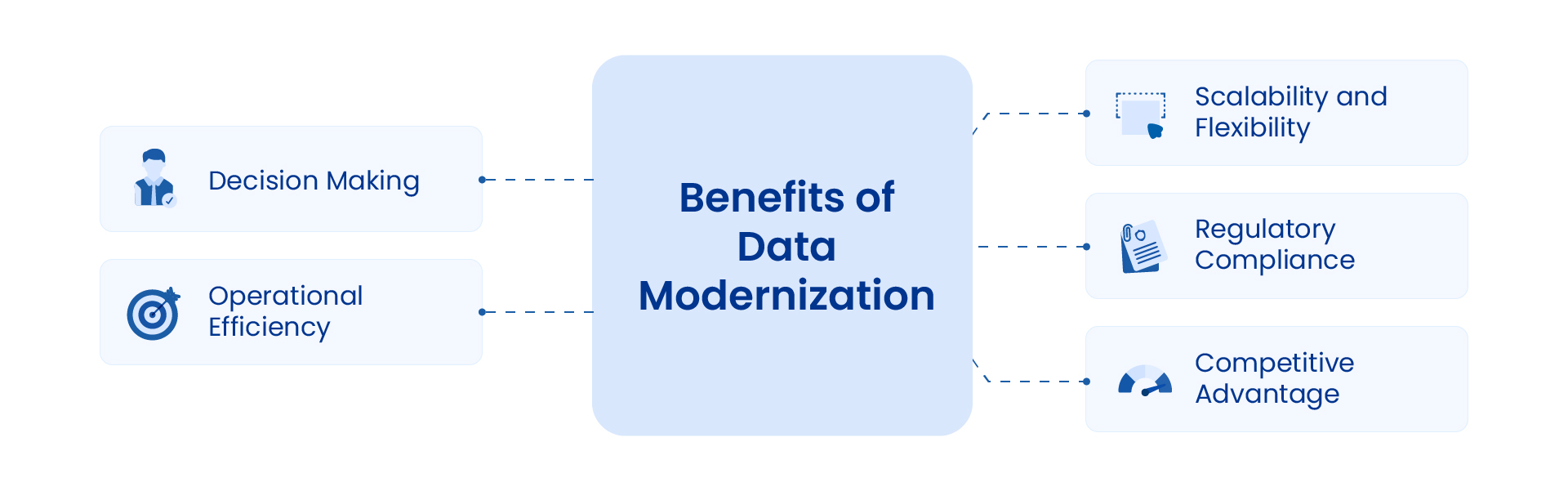
Benefits of Data Modernization
Data modernization offers several key benefits that enhance various aspects of business operations.
-
Decision Making
Data modernization improves the quality and speed of decision-making. By upgrading to advanced data platforms, organizations gain real-time access to accurate and comprehensive data. This accuracy enables faster and more informed decisions, as leaders can analyze up-to-date information and identify trends more effectively.
-
Operational Efficiency
Data modernization automates data management tasks, such as data collection, integration, and transformation, enabling data teams to focus on strategic activities rather than routine data handling.
-
Scalability and Flexibility
Data modernization allows organizations to adjust their data infrastructure dynamically based on workload fluctuations. This flexibility supports adding new data sources and services, ensuring the infrastructure can grow alongside the business.
-
Regulatory Compliance
Data modernization enhances compliance with current regulations and standards. Modern systems include built-in security features and data governance tools that help meet regulatory requirements such as GDPR or CCPA.
-
Competitive Advantage
Adopting modern data solutions helps organizations gain a competitive edge in their market. Improved data analysis and integration capabilities allow businesses to innovate faster as they can better understand trends and respond quickly to customer needs as a result of better data visibility. This foresight helps them stay ahead of competitors and capture new opportunities.
Data Modernization: Key Components
Data modernization involves several key components, each critical in improving data systems.
Data Integration
Data integration combines data from various sources into a unified system, providing a comprehensive view of information across the organization for analysis and decision-making.
Data Cleansing & Quality
Data cleansing and quality processes remove inaccuracies and inconsistencies from data. Clean and accurate data ensures that analyses and insights are based on correct information, leading to better decisions and fewer errors.
Data Consolidation
Data consolidation involves merging data from different systems or departments into a single repository. This centralized repository, or single source of truth (SSOT), delivers a streamlined data architecture that enhances data accessibility, analysis, and utilization.
Data Transformation
Data transformation changes data into a format suitable for analysis and reporting. It aligns data with the requirements of modern data systems and applications. Proper transformation enables practical analysis, integration with other data sources, and compatibility with advanced analytics tools.
Data Migration
Data migration moves data from legacy systems to modern platforms. This is a critical step in the modernization process, as it ensures that valuable data is preserved and accessible in new systems.
Examples of Data Modernization
Data modernization can take many forms, each tailored to specific business needs.
-
Cloud Migration
Moving data and applications from on-premises infrastructure to the cloud enhances scalability, reduces costs, and accelerates data processing.
-
Data Lake Implementation
Creating a centralized repository for structured and unstructured data improves data accessibility, enables advanced analytics, and supports data-driven decision-making.
-
Real-Time Data Processing
Switching from batch processing to real-time data pipelines delivers immediate insights, improves operational efficiency, and enables faster response to market changes.
-
AI/ML Integration
Leveraging artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms to uncover hidden patterns, predict future trends, and automate data processes.
-
Data as a Service (DaaS)
Offering data as a consumable service, like APIs and data feeds, enhances data monetization, improves data accessibility, and accelerates time-to-market for data products.
-
IoT Data Integration
Collecting and analyzing data from connected devices, like wearables and automotive systems, generates valuable insights, optimizes operations, and creates new business opportunities.
Developing a Data Modernization Strategy
A data modernization strategy outlines how an organization will improve its data management practices. It involves a series of steps to upgrade data, tools, and infrastructure.
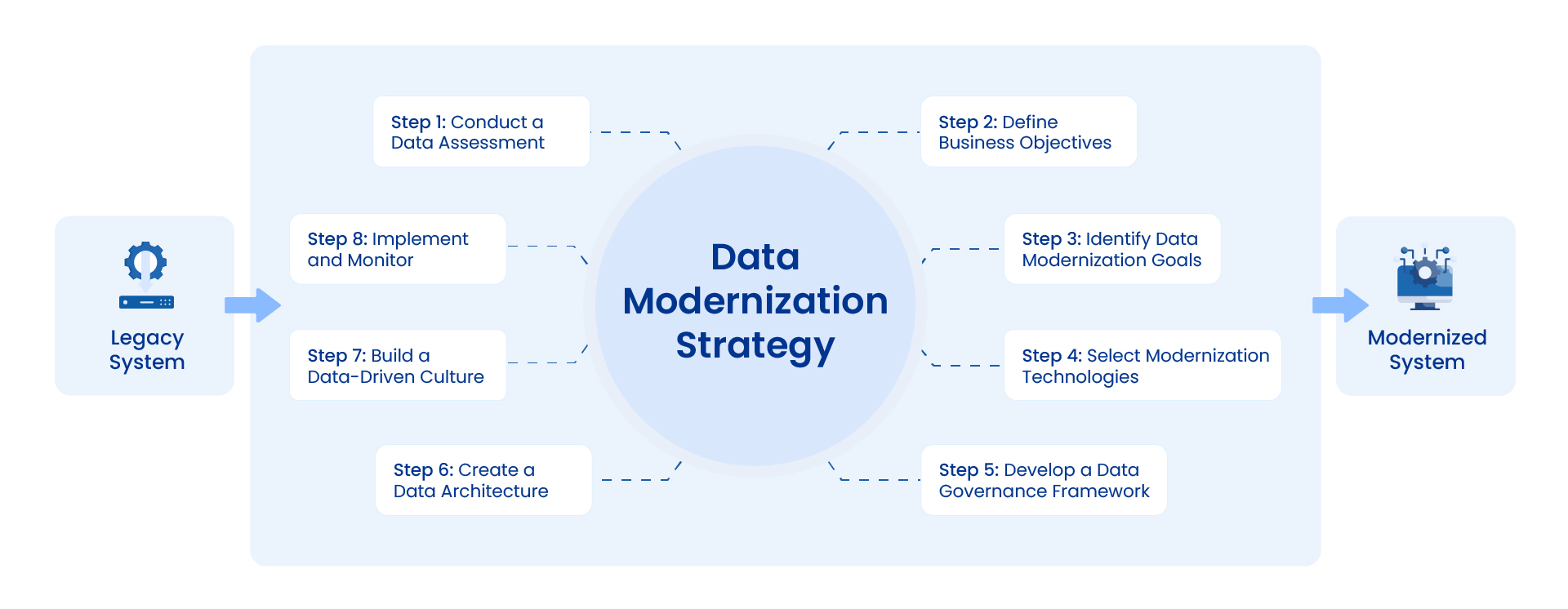
Step 1: Conduct a Data Assessment
This initial step of data modernization involves understanding the current data landscape. Assessing data quality, accessibility, and usability provides a baseline for decision-making and data analysis improvement. Identify data sources, formats, and storage methods, as it provides a clear picture of existing architecture, allowing for data migration, integration, and transformation to support modern analytics and applications.
Step 2: Define Business Objectives
Clearly outline how improved data management will support business goals. Identify specific use cases and desired outcomes, like product development or supply chain optimization. This step ensures that data modernization aligns with the overall business strategy.
Step 3: Identify Data Modernization Goals
Based on the data assessment and business objectives, set clear goals for data modernization. Determine which areas need improvement, such as data quality, accessibility, or analytics capabilities. Prioritize these goals based on their impact on the business.
Step 4: Select Modernization Technologies
Choose the right tools and technologies to support organizations’ goals. Consider cloud platforms, data warehouses, data lakes, and analytics tools, as they provide data storage, automation, analysis, and visualization capabilities. Evaluate their capabilities, cost, and integration with existing systems.
Step 5: Develop a Data Governance Framework
Establish data governance policies and procedures. Define data ownership, quality standards, and security measures. This ensures data reliability, consistency, and protection.
Step 6: Create a Data Architecture
Design a data architecture that supports business needs. This includes data models, data flows, and integration points. It provides a blueprint for storing, processing, and integrating data across systems, supporting efficient data utilization and informed decision-making.
Step 7: Build a Data-Driven Culture
Foster a data-driven culture within the organization. Provide training and education on data literacy and analytics. Encourage data-driven decision-making at all levels.
Step 8: Implement and Monitor
Execute the modernization plan in phases, as this will ensure manageable changes and minimize disruption. Monitor progress and adjust the strategy as needed to optimize the process, guaranteeing alignment with evolving business needs and maximizing the return on investment. Continuously evaluate the impact of data modernization on business outcomes.
Stages of Data Modernization
Data modernization involves several key stages, each essential for successfully upgrading data systems. Here’s a detailed look at each stage:
-
Data Assessment
The first stage is data assessment, where businesses evaluate the current state of their data and systems. The assessment involves identifying all data sources, understanding data quality, and assessing existing infrastructure. Organizations review data storage, usage patterns, and current issues. The data assessment step helps determine what needs to be modernized and sets the foundation for the modernization process.
-
Pre-Migration
In the pre-migration stage, organizations prepare for the actual migration by planning and setting up the necessary processes. Planning includes selecting the right tools and technologies for the new system and designing a migration strategy. Businesses establish data governance policies, define roles and responsibilities, and create a detailed migration plan. Ensuring data quality and cleansing data before migration is critical in this phase.
-
Data Transformation
Data is converted into a format suitable for the new system during data transformation. Transformation involves cleaning the data to remove errors, converting data formats, and integrating data from different sources. The goal is to ensure data is consistent, accurate, and aligned with the new system’s requirements. This step includes mapping data from old formats to new ones and preparing it for migration.
-
Migration
The migration stage involves moving data from the old system to the new one according to the earlier migration plan. Organizations transfer data in batches or all at once depending on the strategy. Users also monitor the migration to ensure data is transferred accurately and without loss. This stage may include testing to confirm that the data in the new system matches the original data.
-
Post-Migration
After migration, the post-migration stage focuses on verifying and optimizing the new system. Organizations conduct thorough testing to ensure the data is correctly integrated and all functionalities work as expected. This stage also involves training users on the new system and addressing any issues. Finally, businesses monitor the new system for performance and adjust as needed to optimize efficiency and usability.
Final Words
Data modernization intelligently manages the migration process, which requires understanding what data organizations possess, organizing it, and determining what to migrate and what to exclude. Businesses must relocate the data, unpack it, and reorganize it in the new environment, ensuring clear communication to all relevant parties about the data’s new location.
Astera, with its interactive, no-code data management platform, offers businesses a simplified solution for complex data modernization tasks. It provides a unified, AI-powered platform for data integration, transformation, warehousing, API and EDI management, and data delivery, helping organizations achieve their data modernization goals efficiently and effectively.
To learn more, schedule a free demo and see how Astera can modernize your data.
Leverage Astera to Transform Your Data
Ready to modernize your data? Schedule a free demo with Astera today to see how our no-code platform makes data management easy and efficient. Start your journey toward better data today!
Request a Demo Astera AI Agent Builder - First Look Coming Soon!
Astera AI Agent Builder - First Look Coming Soon!