
What is Data Stewardship? Roles, Benefits, and Types
Businesses handle massive amounts of data daily. To make informed decisions, this data must be optimized for accuracy and consistency, which requires effective data management. However, for best results, data management must be coupled with data governance, which provides essential frameworks to manage data quality and security. Data stewardship takes it a step further.
What is Data Stewardship?
Data stewardship is the set of practices to manage and oversee data assets within an organization. The goal is to ensure that data is accurate, consistent, accessible, and secure at all times.
Data stewardship is an important component of data governance. While data governance establishes the foundational principles and guidelines for data management to protect data from loss, corruption, theft, or misuse, data stewardship actively implements those principles through routine tasks and activities. However, the roles and responsibilities of a data steward go beyond implementing these policies and procedures. It is also about establishing trust and accountability around managing data in an organization. Thus, data stewards are responsible for the oversight of the entire data lifecycle management, from data collection and storage to usage and disposal.
Why is Data Stewardship Important for Businesses?
Data has evolved from a supporting asset to a strategic foundation for businesses. Its value is immense, often constituting a significant portion, i.e., 87% of an organization’s worth. However, the benefits can only be realized when data is accurate, accessible, and secure.
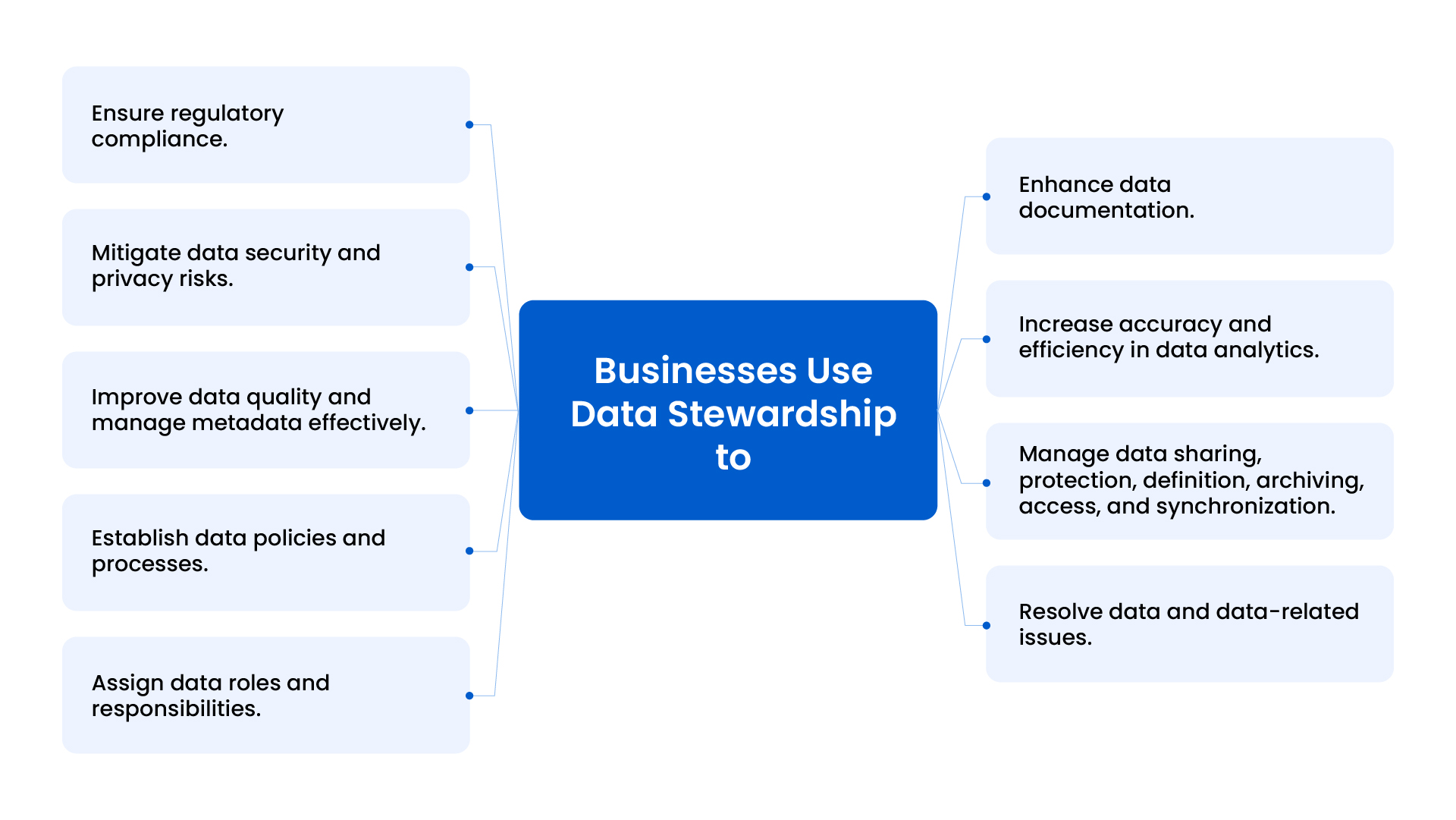
A data stewardship program helps in achieving these objectives. Data stewardship is important:
For Ensuring Data Quality and Integrity
Data stewards safeguard data quality and integrity. They establish and enforce data standards, detect errors, and prevent data from being corrupted.
For Compliance with Regulatory Requirements
Data, especially customer data, is sensitive. Data stewardship helps companies manage and govern data to protect it from breaches and to demonstrate compliance with regulations. Therefore, a data steward’s role is vital in safeguarding organizational reputation and avoiding costly penalties.
For Driving Data-driven Culture
Data stewardship leads to a data-driven culture, empowering employees to make informed decisions. As a result, they become more efficient, make fewer mistakes, and contribute to improved customer satisfaction.
For Optimizing Data Investments
Data stewardship can maximize data return on investment (ROI) if done effectively. It helps businesses identify data improvement opportunities and allocate resources efficiently.
What is a Data Steward?
Data stewards enforce data usage and security policies outlined by enterprise data governance frameworks. Their key function is facilitating IT and business operations collaboration by overseeing data management processes.
The data steward role emerged as a crucial function in the early 2010s as organizations increasingly recognized the immense value of data and the insights it provides. Information governance, of which data stewardship is a core component, became essential for managing the growing value of data.
Typically,
“Data stewards act as custodians of an enterprise’s data, safeguarding it on behalf of all stakeholders. While responsible for maintaining data integrity and accessibility, they do not own the information.”
3 Reasons Organizations Need to Appoint a Data Steward
- When they want to ensure data fitness. Organizations need a dedicated person for data quality management. Without this role, data improvement remains inconsistent. A data steward becomes the primary resource for data health, ensuring that data is accurate, complete, consistent, and accessible for business use.
- When they want to capture every bit of insight. Documenting data knowledge, or metadata, proves essential to ensuring data quality, understanding data lineage, and facilitating effective data governance. Consider a list of numbers 9750 3527, 8596 8608, 3487 8698: without context, it holds little or no value. Adding metadata, such as a column header “Phone_number,” provides immediate clarity. Organizations need data stewards to transform raw data into meaningful information.
- When they want to foster collaboration. Understanding data usage across the business requires cross-functional collaboration. Organizations seek data stewards to act as domain experts to ensure data meets diverse needs. They want them to establish data quality frameworks and standards that serve as guidelines for data creators.
Simply put,
“A data steward serves as the central authority for business data, safeguarding its integrity, preventing chaos, and ensuring accurate, reliable data-driven decisions. Without this crucial role, organizations risk wasting time and money on low-quality data.”
What are the Roles and Responsibilities of a Data Steward?
A data steward must:
- Possess a deep understanding of the data they manage.
- Have strong technical and business skills, including programming, data modeling, and enterprise strategy.
- Possess a broad organizational perspective to ensure data benefits all stakeholders.
- Proactively improve data quality and accessibility through rules, processes, and problem-solving.
- Effectively collaborate with colleagues to ensure data integrity.
The key responsibilities of a data steward revolve around optimizing data management and governance across the business. Besides operational oversight, other responsibilities of a data steward include:
Data Quality Management
Stewards oversee the data lifecycle, defining and enforcing rules for data management. They establish data quality metrics, including acceptable values, ranges, and parameters for data elements.
Privacy, Security, and Risk Management
Data stewards protect data privacy by creating regulations and conventions for data usage, mitigating risks associated with unauthorized access, data breaches, and compliance violations.
Data Coordination and Correction
Stewards often balance data coordination and correction. They maintain data definitions, identify data issues, and ensure adherence to standards. Data stewards work with data architects, BI developers, ETL designers, business data owners, and others to maintain data consistency and integrity. They use data profiling tools to support their efforts.
Partnership with Data Owners
Beyond data management, data stewards contribute to strategic goals. They identify opportunities to use data for competitive advantage.
Data stewards collaborate with data owners, typically senior managers responsible for identifying data needs and usage within their functions, to align data with enterprise goals.
The Dual Nature of Data Stewardship
The data stewardship job description encompasses both defensive and offensive responsibilities. On one hand, stewards protect data from regulatory risks and reputational damage via data governance, educating employees, and fostering a culture of data protection. On the other hand, they facilitate data-driven innovation, inspiring users to leverage data for better decision-making.
It is important to note that the data steward program aligns with the data governance program. This conjunction sets the strategic direction, risk tolerance, and security standards for data.
Types of Data Stewards
Data stewardship roles vary widely based on organizational structure, industry, and data management needs. While the concept of everyone being a data steward holds merit, the four main types of data stewards include:
-
Data Object Data Steward
They oversee the quality, integrity, and consistency of specific data elements or objects within an organization’s data ecosystem.
-
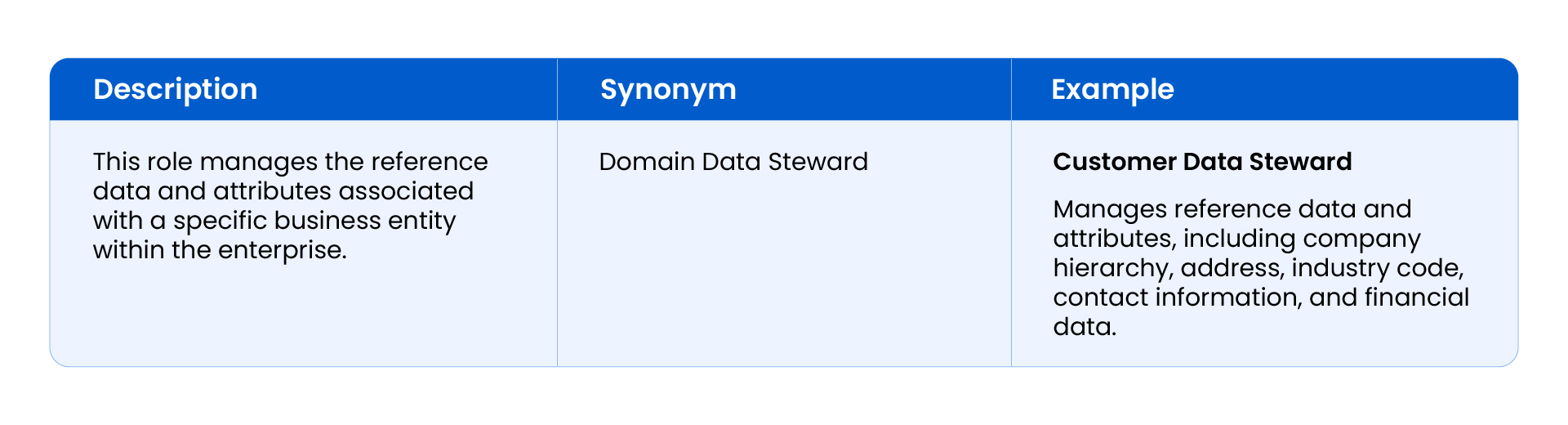
Business Data Steward
They are responsible for ensuring the quality and accuracy of data related to specific business domains or functions.

-
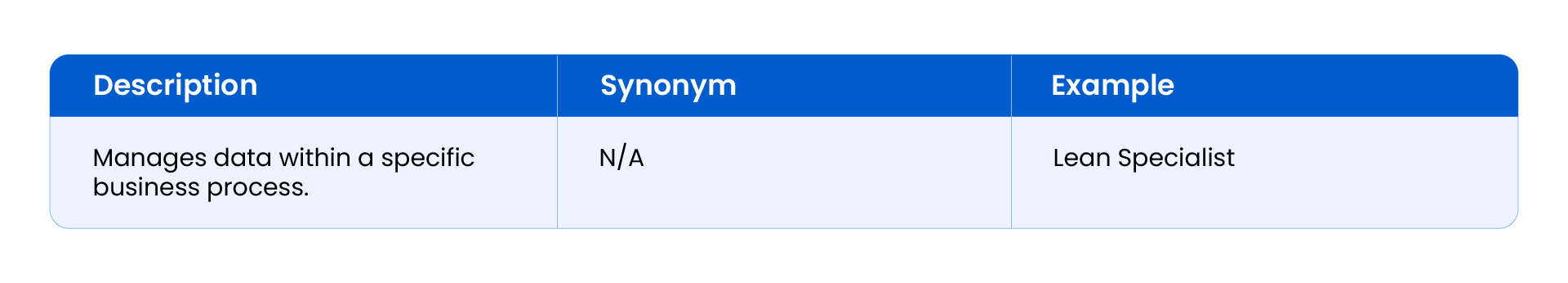
Process Data Steward
Process data stewards are concerned with the data that flows through business processes. They ensure data is collected, processed, and used effectively to support organizational goals.
-
System Data Steward
They focus on the technical aspects of data management, including data quality, consistency, and security.

The four data steward types above represent common roles, but organizations may categorize them differently or combine responsibilities. A data steward’s specific scope and duties depend on the organization’s culture, data governance structure, available resources, and strategic priorities.
Data Steward vs. Data Analyst vs. Data Scientist
Data stewards in organizations are expected to partner closely with data analysts and data scientists. Although all three positions interact with data, their functions within the organization are distinct.
A Walkthrough of The Role of Data Analysts, Scientists and Stewards
Their Responsibilities
Data Analysts are focused on understanding and communicating data-driven insights. They:
- Gather and organize data from various sources.
- Perform data cleaning and preparation.
- Use statistical techniques and data extraction tools to extract and analyze meaningful information.
- Create reports and dashboards to show findings to stakeholders.
Data Scientists take a more analytical and predictive approach. They are involved in:
- Developing and apply advanced statistical models and machine learning algorithms.
- Building predictive models to forecast trends and outcomes.
- Conducting data exploration and discovery to uncover hidden patterns and relationships.
- Collaborating with domain experts to solve complex business problems.
Data Stewards play a custodial and governance role. They primarily:
- Manage data lifecycles from creation to deletion.
- Ensure data quality, consistency, and security.
- Develop and enforce data policies and standards.
Act as a bridge between business users and technical teams.
Their Skills
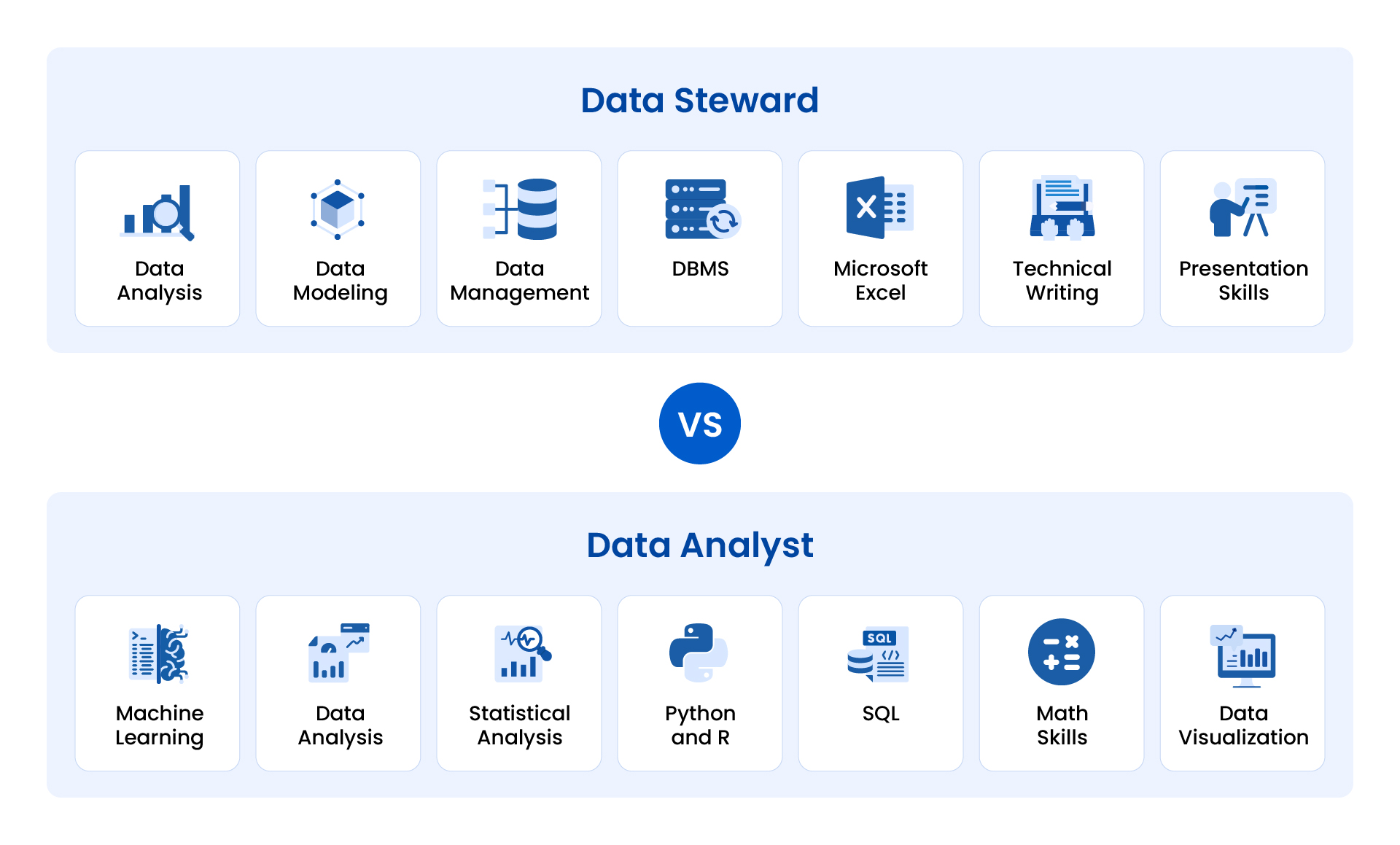
The difference between the skills of data stewards and data analysts can be illustrated as follows:
Take the Next Step in Your Data Journey with Astera
As data grows in volume and complexity, the role of data stewardship will only become more critical. Organizations can optimize data management and position themselves for future growth and innovation by adopting data stewardship as a key priority.
Understanding the critical role of data stewardship is the first step. Organizations must translate this awareness into concrete actions to fully capitalize on its benefits. A robust data stewardship program is essential for achieving a significant competitive advantage.
Astera is a partner in this journey. Its data integration and management solutions are designed to empower data stewards to streamline data operations, improve data quality, ensure compliance with data privacy regulations, and drive business value. By leveraging Astera’s platform, companies can:
- manage data lifecycles
- enhance decision-making
- deliver actionable insights
In short, unlock the full potential of their data.
Ready to equip your data stewards with the data stack they need? Contact us today.
Unleash the Power of Your Data with Effective Data Stewardship
Take control of your data and ensure accuracy across your organization with the Astera Data Stack — view the demo now and experience seamless data management like never before!
View Free Demo


