
Master Data Management for Beginners
One of the significant challenges for an organization is to create a single source of truth while maintaining its reliability, accuracy, and quality. Master data management (MDM) might be your silver bullet when simplifying data management.
In this article, you’ll discover master data management, its main components, the benefits of master data management for your business, and some key challenges associated with the practice is.
What Is Master Data Management (MDM)?
Let’s start with understanding what master data management is.
Master data management is the technology that ensures consistency of enterprise data – across multiple systems, applications, databases, functional departments, and geographies.
Today, enterprise data distributes across versatile applications and systems, such as ERPs and CRMs. As a result, there’s a high probability that data across different departments can become easily fragmented, redundant, and often outdated. Your business may find it extremely challenging to respond even to the most rudimentary yet critical inquiries about any performance indicators in such a scenario. For instance, master data management may answer essential questions of business, such as “what is the profit margin on products/services?” and “which business unit is the most profitable?”.
So, how do you keep the data accurate, coherent, and timely, significantly when data sources are increasing, and it’s become trickier to manage them consistently? Master data management makes it easier to tackle these challenges by creating a unified master reference source for critical data. However, one essential requirement of master data management is good data governance that ensures data validity and security.
The types of master data management usually differ depending on the type of industry your organization operates in. However, all types of master data share some features such as:
- Complexity: Master data consists of large data sets with multiple variables, making it complex.
- High Value: Master data is often used time and again for analysis. It is a crucial part of an organization’s daily operations.
- Not Volatile: Master data doesn’t change often; it changes lesser than other data.
- Non-Transactional: Master data does not consist of transactional data; however, it is often part of the transaction process.
Understanding Master Data
Master data is the central data within a company that defines domains involved in operating a business. This data changes rarely and can include reference data, which can be used to relate to information that falls outside the enterprise data domains and is essential to running the business. By nature, it’s not transactional; however, it does define transactions.
Most software systems used in a company have master data shared and used by many applications. A common example of master data is your ERP system which may have lists of data such as customer master data, employee master data, item master data, and account master data.
Master data generally covers data falling into four main categories of a business, which are further sub-categorized into the following subject areas:
- Parties: Groups who carry out business with the organization, such as customers, prospects, suppliers, associates, etc.
- Places: Actual places and the way they are segmented, like geography, location, sites, zones, etc.
- Things: Items that the business sells or manages, such as products, services, or assets
- Financial and Organizational: Reporting and accounting classifications that comprise organizational structures, sales regions, chart of accounts, cost centers, business units, profit centers, price lists, etc.
Difference Between Master Data and Reference Data
Every business has data related to consumers, products, workers, etc., rarely stored in a single place. This data is usually distributed across different divisions in numerous applications, databases, and even physical media like documents and reports. What makes it more challenging is that diverse aspects of the company may have different ideas and descriptions for the same business object. For instance, a worker might have records in multiple company management systems while, in reality, they are the same individual.
This is where reference data steps in. It’s any type of data used to classify other data items set up in a database. In other words, it’s solely used for linking data in a databank to the one outside the confines of the business.
Master data includes relevant business entities, whereas reference data comprises permissible values and attached textual descriptions. In other words, master data is shared by several systems, applications, and procedures in the business. In contrast, reference data is a kind of master data used by transactional or master data objects.
What Data Should You Manage as Master Data?
Generally, master data is usually a tiny share of your complete data in terms of volume. However, it’s challenging to preserve and manage; therefore, some choose master management tools.
It is recommended to use the following benchmark of master data management strategy, which guide on how to manage master data:
- Behavior Data: You can describe master data by interrelating with other data types.
- CRUD Cycle: You can also describe master data by its lifecycle, i.e., how it’s created, read, updated, deleted, and searched (the CRUD cycle).
- Cardinality: Cardinality defines the number of items in a set. When it declines, the probability of an item being considered master data also declines.
- Lifespan and Volatility: Unlike transactional data, master data has less volatility.
- Intricacy: Simple and less intricate objects are easier to collect, manage, and tally. Hence, they are generally not categorized as master data.
- Value: Precious data items are more likely to be considered master data.
- Reuse: If any data is reused several times in multiple systems, it should be managed as master data.
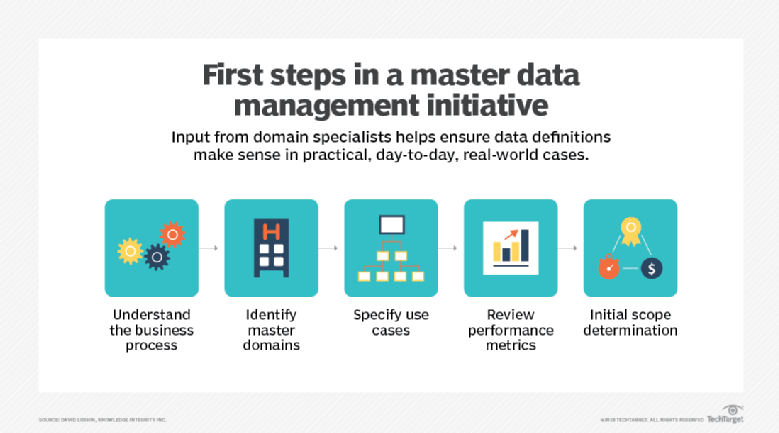
First steps of master data management initiative. Source: TechTarget
Essentials of Master Data Management
Some of the critical components or best practices of a master data management (MDM) system for an enterprise are:
- Flexible Data Model: To manage and maintain master data, you need a very flexible data model.
- Data Quality Module: It allows you to monitor the quality of the incoming data to ensure that the data is credible. In addition, it should also include a validation rules engine so that you can also describe the data quality rules for your master data according to the business requirements.
- Data Integration Module: It allows you to integrate master data with other systems. Ideally, it should have an easy-to-use interface and a robust processing engine to execute high-volume data integration jobs.
- Workflow Engine: Workflows allow users to package several activities within a single flow. MDM workflows include several functions ranging from validating to merging entities. A robust workflow engine will give you greater flexibility to model your procedures into the workflows.
In short, make sure that the data management software or system you are selecting offers the utmost performance, scalability, security, accessibility, and reporting capabilities.
Why is Master Data Management Important: Benefits of Master Data Management
Some key benefits of master data management (MDM) include:
- Unified and Consistent Information Across Numerous Networks
You need accurate and consistent data to set your business apart. Using master data management (MDM), you can easily manage data from several source systems and create a master set of authenticated, unique first-class data that other departments can utilize.
- A Better Understanding of Your Customers
You can create a holistic view of your consumer data by harmonizing customer records with the information supply chain and generating insightful reports. This can help you get a more in-depth understanding of your customers’ preferences and personas.
- An Integrated View of Business Data Assets
Master data management enables you to create dependable views of your organizational data assets to conduct business processes efficiently. Product master data management (MDM) assists in the formation of a cohesive view of consumer, supplier, material, and product data which may otherwise exist in different divisions and entities.
- Improved Data Reliability and Trust
Poor quality data has an undesirable impact on business management, be it client relations or corporate policymaking. MDM ensures consistent, credible, and quality data is delivered across all systems and departments. Thus, businesses can make reliable data-driven analyses.
Challenges Associated with Managing Master Data
Despite the benefits that master data management offers, implementing a master data management (MDM) solution is no easy feat. Here are a few challenges that you may encounter during the process:
- Complexity: Managing master data in multiple systems and formats can be challenging, as it requires standardizing data according to the business requirements.
- Data Overlapping: There’s also a high chance of data overlapping as multiple systems store the same entities. Using an MDM solution with extensive data quality management features can help resolve data duplication issues.
- Lack of Data Model: A master data management (MDM) model can simplify integration by defining different tiers of master data. Lack of a data model in place can complicate management.
- Criteria: Usually, it isn’t easy to agree on domain values stored across different systems.
- Authority and Data Governance: Poor data authority (stewardship, possession, procedures) related to master data results in complications within the business.
- Lack of Skilled Individuals: It is also challenging to find experienced specialists and implementation allies to help accomplish ventures.
- Choice of Technology: There are various solutions available in the MDM industry, so it can be hard to choose one absolute front-runner.
- Other Challenges: Some other challenges include deciding where to begin, prioritizing, and emphasizing as well as educating the employees on the importance of master data management (MDM).
Master data management (MDM) solutions simplify business data by pooling data with several formats from heterogeneous data sources and creating an integrated view, eliminating data silos. This leads to fewer blunders and less redundancy in corporate procedures.
 Astera AI Agent Builder - First Look Coming Soon!
Astera AI Agent Builder - First Look Coming Soon!


