
What is Metadata Governance?
What is Metadata Governance?
Metadata governance is the systematic approach to managing metadata, or data about data, to ensure it is accurate, consistently formatted, and securely stored. The main goal of metadata governance is to improve data quality, ensure data privacy, and streamline metadata management.
As metadata provides the necessary details about data, such as when it was created, by whom, and its content or purpose, it becomes easier for employees to find, understand, and trust the data they use. It gives the needed context and unique characteristics to data. For example, in a corporate setting, metadata about a sales report could include information about its creation date, the department that created it, and the type of data it contains.
Metadata as a Foundation of Data Governance
Metadata serves as the foundation of data governance by offering the contextual framework for understanding, managing, and using data within an organization. It guides the data governance structure with essential data attributes and usage information, enabling informed decisions about data assets.
In data governance, metadata ensures that data definitions and relationships are consistently applied across the organization, eliminating ambiguities and fostering a unified approach to data interpretation. It also enhances data discoverability, allowing users to quickly find relevant data for analysis, reporting, and decision-making.
Importance of Metadata Governance
Governing metadata is an important component of the data governance framework. Without proper metadata governance, organizations risk data misinterpretation, compliance breaches, and inefficiencies in data use. For instance, without clear metadata governance, two departments can use the same data differently, leading to inconsistencies and potential errors in reporting.
Metadata governance ensures consistency by defining and enforcing rules for how data is described, accessed, and used across an organization. It also encompasses procedures that manage data’s lifecycle, enabling uniform understanding and use of data, thus preventing discrepancies in how different departments interpret and report data.

Main Components of Metadata Governance
Effective metadata governance includes the following six components:
Metadata Standards and Guidelines
These are rules outlining how metadata should be structured and formatted. They determine what metadata to collect, how to classify and categorize it, and conventions for naming and describing it.
Roles and Responsibilities
Clearly defined roles ensure each stakeholder understands their part in metadata governance. This step includes defining who creates, maintains, accesses, and makes decisions about metadata.
Metadata Repository
A centralized database stores and manages metadata. It should be easily accessible to stakeholders and equipped with search capabilities for finding and retrieving specific metadata.
Processes and Procedures
It details how metadata is created, updated, and managed. They also define how metadata quality is unaffected through validation, discrepancy resolution, and change tracking.
Tools and Technology
Systems and software used to create, manage, and access metadata. These tools should support organizational standards and processes while being user-friendly.
Metrics and Performance
These assess the effectiveness of metadata governance. Data quality metrics allow organizations to measure the health of metadata and maintain its accuracy. The measures generally include metadata accuracy, completeness, consistency, and stakeholder engagement level.
Advantages of Effective Metadata Governance
Implementing effective data governance brings numerous benefits to the organization by streamlining the operations and optimizing the data as a strategic asset.
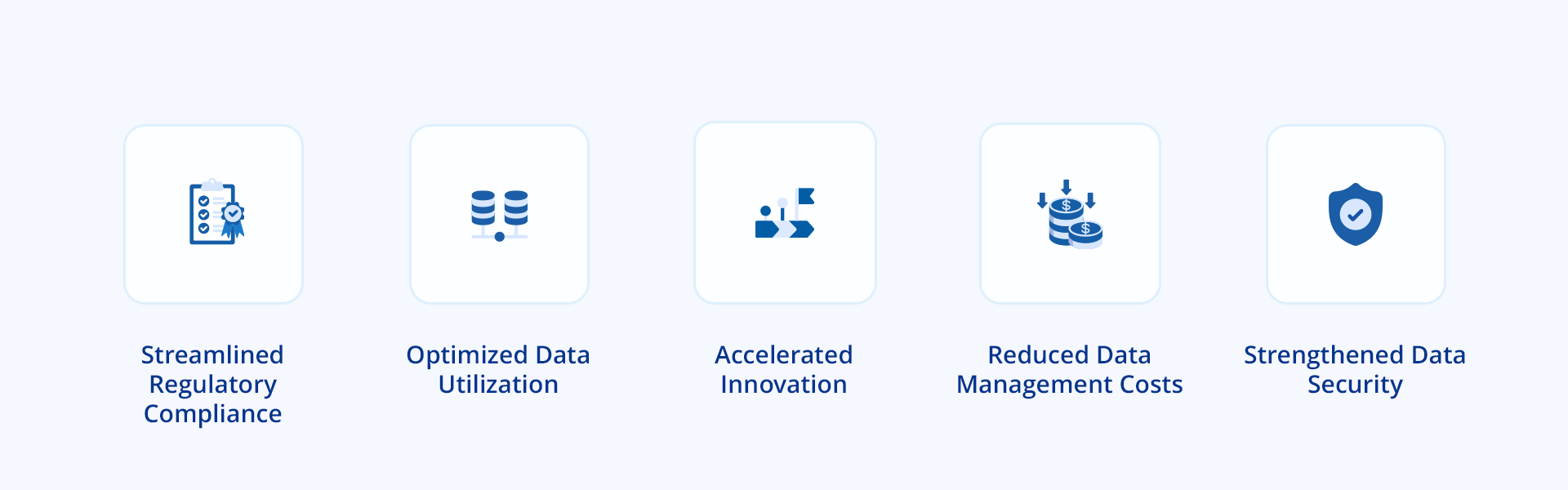
Improved Data Quality
By providing clear context and meaning for data, metadata governance ensures accurate, consistent, and complete information. This reliable foundation leads to more trustworthy analysis and insights.
Faster Decisions
Finding and understanding the data an organization needs becomes easy with metadata governance, reducing search time and allowing businesses to make quicker, data-driven decisions.
Stronger Collaboration
Through metadata governance, everyone in the organization uses and interprets data the same way. This shared knowledge base allows for more effective teamwork and consistent use of data across various projects and initiatives.
Easy Compliance
In industries like power and energy, data privacy regulations are important. Metadata governance helps manage and control data effectively, ensuring compliance with legal requirements.
Usable Data
High-quality, well-documented data becomes more valuable with strong metadata governance, opening doors to monetization opportunities with customers, partners, and other stakeholders.
Enriched Data Management
Strong metadata governance strengthens the entire data management approach.
- Solid Foundation: By meticulously managing metadata, organizations build a strong base for their data. A strong base improves the organization, quality, and usability of information.
- Clear Guidelines: Metadata governance sets clear rules for handling data, making it easier and faster to manage the data assets.
- Improved Workflows: Metadata governance optimizes the data lifecycle from creating and storing data to accessing and disposing of it. An optimized system leads to smoother data workflows and a more efficient system.
Five Steps to Implement Metadata Governance
Setting up a successful metadata governance program is a strategic process that requires thoughtful planning, precise action, and continuous oversight.
- Assess the Current Metadata Landscape
The first step is to take stock of the existing metadata landscape. This involves identifying what metadata is currently being captured, how it’s being stored, and the systems in use.
For example, a retail company examines its product information management system to understand how product attributes, such as size, color, and price, are described and categorized. This initial assessment helps pinpoint gaps and opportunities for improvement.
- Define Clear Goals and Objectives
Next, organizations must outline specific goals and objectives for their metadata governance. An example objective could be enhancing data quality for better analytics or improving data sharing across departments.
Establish specific goals like enhancing product metadata accuracy to boost online shopping experiences, providing a focused direction, and enabling progress tracking.
- Establish a Governance Structure
Creating a governance structure means defining who is responsible for managing and overseeing metadata within the organization. This step involves assigning roles like a metadata manager or governance committee and detailing their responsibilities.
For instance, the metadata manager might ensure that product metadata across all online platforms remains consistent and up to date while the governance committee oversees the overall strategy and resolves any disputes.
- Develop and Enforce Policies and Standards
With roles and responsibilities in place, the next step is to develop clear policies like metadata access, quality, and distribution. These guidelines dictate how metadata should be formatted, the taxonomy to be used, and procedures for updating metadata.
A financial services firm, for instance, would establish policies around tagging financial transactions with metadata that includes the transaction type, amount, date, and involved parties, ensuring consistency and facilitating easier reporting and analysis.
- Regularly Review and Refine Practices
Metadata governance isn’t a set-it-and-forget-it process. Regular reviews and updates are required to ensure the practices remain relevant and effective. This step could involve periodic audits of metadata quality, surveys of users to understand new needs, or assessments of the governance structure to identify areas for improvement.
For example, a media company would review its content metadata practices annually to ensure that new content types are adequately captured and described.
Opportunities in Metadata Governance
Companies can optimize their data management resources and gain a competitive edge by strategically leveraging opportunities in metadata governance.
Encouraging Team Collaboration
One of the key opportunities lies in collaboration across different departments and teams. When diverse teams come together to share their knowledge and best practices about metadata, the organization benefits from a more comprehensive understanding of its data assets. This collaborative approach can develop standardized metadata practices keeping them consistent across the organization, enhancing overall data quality management.
For instance, creating cross-functional working groups dedicated to metadata governance can facilitate discussions on common challenges and opportunities. These groups can work on developing shared metadata standards, guidelines, and vocabularies that all departments can adopt, creating consistency and facilitating smoother data integration efforts.
Advanced Metadata Solutions
Modern data management tools and platforms offer features and capabilities that help organizations govern and manage data, including metadata. In contrast, dedicated metadata management tools offer functionalities such as automation of metadata collection and processing, enhanced data cataloging, and more efficient metadata asset integration. These features significantly reduce the manual effort involved in metadata governance and management, allowing teams to focus on more strategic data governance initiatives.
Implementing a metadata management solution that integrates seamlessly with existing data systems can simplify cataloging data assets, maintaining up-to-date metadata records, and providing users easy access to the information they need. For example, automated metadata tagging and classification systems can help organizations quickly categorize their data assets based on predefined rules, making data easier to find, understand, and use.
Strategies for Effective Metadata Governance
To fully capitalize on the opportunities, organizations should consider the following strategies:
Promote Metadata Literacy: Educate all employees on the importance of metadata and its role in effective data governance. Organizations can provide training on how to create, use, and manage metadata correctly.
Establish Clear Metadata Governance Policies: Develop and implement clear policies that outline metadata management roles, responsibilities, and procedures. Such policies enable everyone to understand their part in maintaining high-quality metadata.
Measure Success: Define clear metrics to measure the effectiveness of metadata governance initiatives. Businesses can track improvements in data quality, reductions in data discovery times, or increases in user satisfaction with data systems.
Final Words
Integrating metadata governance into a company’s data governance strategy transforms the value of its data. It enhances data reliability and usability, making it a strategic asset that can drive decision-making and innovation. The journey towards effective metadata governance requires a thoughtful approach, which involves understanding the current landscape, refining practices, and leveraging new opportunities for collaboration and technological enhancement.
Astera simplifies metadata governance efforts by automating metadata discovery, categorization, and management – empowering users to complete these tasks more accurately and in less time. With Astera, businesses can establish a metadata governance framework that enhances data quality and facilitates faster decision-making.
Implement Metadata Governance to Optimize Data Management
Looking to enhance metadata governance? Try Astera for free for 14 days and optimize your data management. Experience how Astera streamlines data governance processes.
Learn More Astera AI Agent Builder - First Look Coming Soon!
Astera AI Agent Builder - First Look Coming Soon!

