
The Role of Data in Personalized Banking
With over 70% of customers emphasizing the importance of personalized offers in banking, it’s evident that people highly value tailored experiences from their financial institutions. However, despite this strong customer preference, only 14% of banks have embraced personalized banking.
This reveals a significant gap between customer expectations and the services currently provided by the finance industry. Bridging this gap requires leveraging the role of data.
Personalized banking experiences rely on utilizing customer information and insights derived from data. These insights are crucial in shaping services that align more precisely with individual preferences and needs.
What is Personalized Banking?
Personalized banking focuses on delivering unique experiences to customers based on their financial needs and preferences outlined by behaviors. This personalized approach goes beyond the one-size-fits-all approach of traditional banking services.
Banks collect vast amounts of customer data, ranging from transaction history to online browsing behavior. By leveraging this data for analytics, banks can gain valuable insights into consumer behavior and provide customized recommendations and offers.
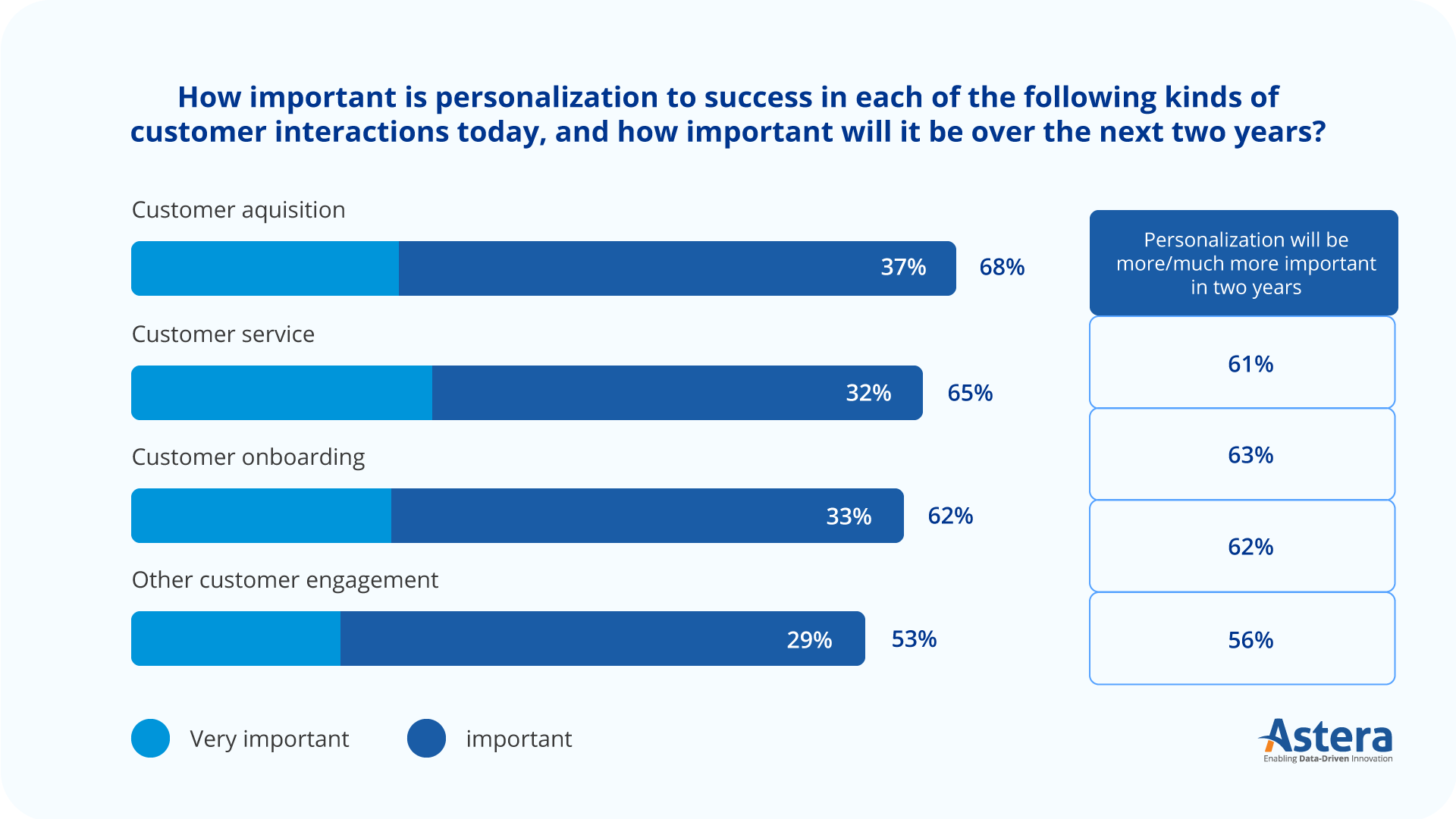
Modern banks recognize the importance of personalization in every aspect of their operations—be it customer acquisition, service, onboarding, or overall engagement.
Benefits of Personalized Banking
- Customer Satisfaction and Loyalty: Personalization enhances customer satisfaction by addressing specific financial needs, making customers feel valued and understood. This tailored approach fosters a deeper connection with the bank, leading to increased loyalty and retention rates. Banks can also offer rewards programs where customers receive discounts, cashback, or exclusive deals based on their spending patterns.
- Tailored Financial Advice: Banks can provide individualized financial guidance, such as personalized investment strategies based on a customer’s income, risk apetite, and goals. This not only improves customer satisfaction but also increases the likelihood of achieving financial goals.
- Increased Revenue Opportunities: Through data analysis, banks can identify additional services or products that align with customers’ needs, leading to cross-selling and upselling opportunities. This targeted approach benefits both customers and the bank by expanding product offerings and revenue streams.
- Financial Literacy and Education: Personalized banking includes providing dedicated educational materials to improve customers’ understanding of complex financial concepts. Educating customers contributes to their financial well-being and strengthens long-term relationships.
Source: info.blend.com
How are Banks Using Personalized Banking?
Targeted Product Recommendations
Banks analyze customer spending patterns and offer personalized recommendations for credit cards, loans, or investment products that align with the customer’s financial goals.
For instance, imagine a customer who frequently shops at grocery stores and spends a significant portion of their income on groceries. The bank would analyze this customer’s transaction history and identify their spending patterns. Based on this information, they might recommend a credit card that offers cashback or rewards specifically for grocery purchases. This personalized recommendation not only helps the customer maximize their savings, but also strengthens their relationship with the bank.
Customized Marketing Campaigns
Banks personalize their marketing efforts by sending targeted offers based on customers’ transaction history and preferences. For example, a customer who frequently travels may receive offers for travel insurance or foreign currency services.
Consider a customer who frequently uses their credit card to book flights and hotels. A bank utilizing personalized banking would analyze this customer’s transaction history and identify their travel-related expenses. Armed with this knowledge, the bank could tailor their marketing campaigns to offer the customer exclusive travel benefits, such as discounted travel insurance or preferential foreign currency exchange rates. By providing personalized offers that align with the customer’s interests, the bank enhances the customer’s experience and increases the likelihood of them engaging with the bank’s services.
Personalized Customer Service
Banks use customer data to provide personalized customer service experiences. For instance, a customer calling the bank’s helpline will be routed to a representative who specializes in their specific financial needs.
Imagine a customer who recently started a small business and needs guidance on managing their business finances. With personalized banking, when this customer calls the bank’s helpline, their call is directed to a representative who specializes in assisting small business owners. This representative would have a deep understanding of the challenges and opportunities faced by small businesses, allowing them to provide tailored advice and support to the customer.
Overcoming Challenges in Data-Driven Personalized Banking
While data-driven banking offers numerous benefits, it also poses challenges. Banks need to address these roadblocks effectively to ensure their strategies are successfully impelemented.
Legacy Infrastructure:
Older data processing systems often struggle with:
- Utilizing Unstructured Data: Inability to process and derive insights from the rapidly growing unstructured and alternative data sets.
- Open Data Sharing: Lack of capabilities for open data sharing, hindering collaboration and integration with external sources.
Financial institutes should invest in modernizing their infrastructure to handle unstructured data efficiently. Upgrading data integration systems and adopting advanced analytics tools can aid in this process. Additionally, fostering partnerships and embracing open APIs can facilitate seamless integration with external sources.
Strict Data Regulations:
Increasing concerns about data breaches have led to:
- Consumer Caution: Heightened consumer wariness in sharing personal data due to high-profile instances of data theft and breaches.
- Regulatory Compliance Burden: Stricter regulations necessitate more comprehensive measures to safeguard customer information, adding complexity and cost to operations.
Implementing robust data protection measures such as advanced encryption technologies and multi-factor authentication is crucial. Banks should also regularly audit data access and invest in monitoring systems to ensure compliance. Transparent communication about data privacy policies is essential to build trust and reassure consumers about the security of their information.
Access to Third-Party Data:
Issues in accessing and leveraging external data arise due to:
- Disjointed Tools: Challenges in performing real-time analytics and democratizing financial decisions due to fragmented tools and systems.
Banks can diversify their data sources by reducing dependency on single vendors or technologies. Integration of unified analytics platforms and adopting standardized tools across business units can streamline data access and enable real-time analytics for better decision-making.
Data Silos:
Internal challenges revolve around:
- Complex Workflows: Highly intricate processes hinder collaboration and smooth data flow.
- Disparate Technologies: Using multiple systems across various business units creates data silos, preventing cohesive insights and decision-making.
Banks should focus on streamlining workflows by implementing centralized data management systems. Integration of technologies across departments and fostering a culture of data sharing and collaboration can break down silos, enabling better data flow and cohesive insights for decision-making.
The Role of ETL in Personalized Banking
ETL is a process of extracting data from different sources, transforming it into a standard format, and then loading it into a target system. In personalized banking, ETL plays a crucial role in enabling data-driven decision-making and delivering personalized experiences to customers.
Extract
The extraction phase involves gathering customer-centric data from numerous sources. This process includes pulling essential information from internal systems, such as transaction logs, customer databases, and account histories.
External sources also play a vital role in enriching this data pool. These sources might include social media platforms, where individuals may engage with financial institutions or express preferences that can inform personalized services. Moreover, data from credit bureaus and other financial institutions can offer insights into credit histories, loan obligations, and other relevant financial behaviors, contributing significantly to the holistic view of a customer’s financial profile.
This extracted data forms the foundation upon which various analytics and machine learning models operate.
Transform
During the cleansing process, data is carefully examined, and any inconsistencies, errors, or duplicates are identified and corrected. For example, if a customer’s name is misspelled in one source, the ETL process can be designed to ensure consistent customer information across all relevant datasets. This attention to detail is essential in personalized banking, as even small errors can lead to incorrect recommendations or decisions.
is another critical step in the ETL process. It involves combining data from multiple sources. Integration can be time-consuming, especially when dealing with large volumes of data. However, ETL tools, such as Astera, have advanced significantly, making integration more efficient and seamless.
During the transformation phase, companies can apply enrichment as an additional step. It involves enhancing the data with additional information to provide a more comprehensive view. For example, demographic data, such as age, gender, or location, can be added to customer records to enable better segmentation and targeting.
Load
Finally, the transformed data is loaded into a centralized data warehouse or data mart, where it can be further analyzed and utilized for personalized banking initiatives. This unified data enables banks to gain a 360-degree view of their customers, leading to meaningful insights and personalized recommendations.
How Does Astera Help Financial Institutions with Personalized Banking?
Astera empowers financial institutions to craft personalized banking experiences by offering a comprehensive suite of features, ensuring seamless integration, data security, compliance, and operational efficiency.
Here’s how Asters cater to your needs:
- Intuitive Drag-and-Drop Interface: Astera streamlines operations with a no-code interface, allowing seamless data management to facilitate personalized banking solutions.
- Extensive Connectivity to Diverse Data Sources: Seamlessly integrate data from various sources to ensure a comprehensive view of your customer data. Astera facilitates connectivity, bridging gaps between disparate data sources for a unified perspective.
- Library of Pre-Built Transformations: Accelerate data processing with our pre-built transformations, effortlessly manipulating and enriching data for actionable insights.
- Flexible Data Pipeline Builder for ELT and ETL: Construct tailored data pipelines with an industry0grade ELT and ETL engine. Astera ensures efficient data processing from extraction to loading, meeting specific institutional needs.
- Simplified Data Mapping: Streamline complex data mapping processes for precision and accuracy, enabling efficient mapping of data elements.
- Efficient Workflow Automation: Increase operational efficiency with automated workflows, orchestrating processes seamlessly for a more personalized service.
- Real-Time Change Data Capture (CDC): Stay updated with Astera’s Change Data Capture feature, integrating real-time changes for swift responses and personalized services.
- Secure Managed File Transfer (MFT): Safeguard critical data with our Managed File Transfer capabilities, ensuring the secure flow of sensitive information within your data ecosystem.
- Robust Security Measures: Prioritize data security with encryption protocols, role-based access control, and publishing workflows deployed on-premise, ensuring utmost security for personalized banking data.
- Compliance Alignment (e.g., GDPR): Astera helps align with global data regulations such as GDPR, ensuring banking services are delivered ethically and responsibly.
Ready to revolutionize your banking experience? Experience the power of personalized services with Astera. Sign up for a demo or a 14-day- free trial now to discover the future of finance!
 Astera AI Agent Builder - First Look Coming Soon!
Astera AI Agent Builder - First Look Coming Soon!

